A virus-encoded inhibitor that blocks RNA interference in mammalian cells
- PMID: 15919892
- PMCID: PMC1143619
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7371-7379.2005
A virus-encoded inhibitor that blocks RNA interference in mammalian cells
Abstract
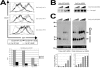
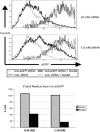
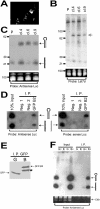
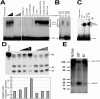
Nodamura virus (NoV) is a small RNA virus that is infectious for insect and mammalian hosts. We have developed a highly sensitive assay of RNA interference (RNAi) in mammalian cells that shows that the NoV B2 protein functions as an inhibitor of RNAi triggered by either short hairpin RNAs or small interfering RNAs. In the cell, NoV B2 binds to pre-Dicer substrate RNA and RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)-processed RNAs and inhibits the Dicer cleavage reaction and, potentially, one or more post-Dicer activities. In vitro, NoV B2 inhibits Dicer-mediated RNA cleavage in the absence of any other host factors and specifically binds double-stranded RNAs corresponding in structure to Dicer substrates and products. Its abilities to bind to Dicer precursor and post-Dicer RISC-processed RNAs suggest a mechanism of inhibition that is unique among known viral inhibitors of RNAi.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The contributions of dsRNA structure to Dicer specificity and efficiency.RNA. 2005 May;11(5):674-82. doi: 10.1261/rna.7272305. Epub 2005 Apr 5. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15811921 Free PMC article.
-
HCV core protein interacts with Dicer to antagonize RNA silencing.Virus Res. 2008 May;133(2):250-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Mar 5. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18325616
-
Nodamura virus B2 amino terminal domain sensitivity to small interfering RNA.Microbiol Immunol. 2015 May;59(5):299-304. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12253. Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25753649
-
MicroRNAs: Loquacious speaks out.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 9;15(15):R603-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.044. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16085484 Review.
-
[RNA binding proteins in the RNA interference phenomenon].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):595-608. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913219 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic potential of RNA interference.FEBS Lett. 2005 Oct 31;579(26):5996-6007. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.004. Epub 2005 Aug 15. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16115631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral RNA interference in disease vector (Asian longhorned) ticks.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Dec 3;17(12):e1010119. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010119. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34860862 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionarily conserved function of a viral microRNA.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(20):9823-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01144-08. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18684810 Free PMC article.
-
Application of nucleic-acid-based therapeutics for viral infections in shrimp aquaculture.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2009 Jan-Feb;11(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s10126-008-9155-0. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2009. PMID: 18941835 Review.
-
Deformed wing virus genotypes A and B do not elicit immunologically different responses in naïve honey bee hosts.Insect Mol Biol. 2025 Feb;34(1):33-51. doi: 10.1111/imb.12948. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Insect Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39072811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baulcombe, D. 2002. Viral suppression of systemic silencing. Trends Microbiol. 10:306-308. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, E., A. A. Caudy, S. M. Hammond, and G. J. Hannon. 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409:363-366. - PubMed
-
- Carmell, M. A., and G. J. Hannon. 2004. RNase III enzymes and the initiation of gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11:214-218. - PubMed
-
- Carthew, R. W. 2001. Gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13:244-248. - PubMed
-
- Denli, A. M., and G. J. Hannon. 2003. RNAi: an ever-growing puzzle. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28:196-201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

