The minor receptor group of human rhinovirus (HRV) includes HRV23 and HRV25, but the presence of a lysine in the VP1 HI loop is not sufficient for receptor binding
- PMID: 15919894
- PMCID: PMC1143622
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7389-7395.2005
The minor receptor group of human rhinovirus (HRV) includes HRV23 and HRV25, but the presence of a lysine in the VP1 HI loop is not sufficient for receptor binding
Abstract
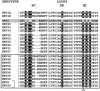
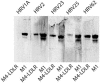
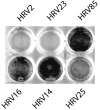
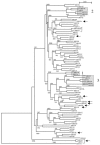
Like all 10 minor receptor group human rhinoviruses (HRVs), HRV23 and HRV25, previously classified as major group viruses, are neutralized by maltose binding protein (MBP)-V33333 (a soluble recombinant concatemer of five copies of repeat 3 of the very-low-density lipoprotein receptor fused to MBP), bind to low-density lipoprotein receptor in virus overlay blots, and replicate in intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1)-negative COS-7 cells. From phylogenetic analysis of capsid protein VP1-coding sequences, they are also known to cluster together with other minor group strains. Therefore, they belong to the minor group; there are now 12 minor group and 87 major group HRV serotypes. Sequence comparison of the VP1 capsid proteins of all HRVs revealed that the lysine in the HI loop, strictly conserved in the 12 minor group HRVs, is also present in 9 major group serotypes that are neutralized by soluble ICAM-1. Despite the presence of this lysine, they are not neutralized by MBP-V33333 and fail to replicate in COS-7 cells and in HeLa cells in the presence of an ICAM-1-blocking antibody. These nine serotypes are therefore "true" major group viruses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive bioinformatic identification of minor receptor group human rhinoviruses.FEBS Lett. 2009 Aug 6;583(15):2547-51. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.015. Epub 2009 Jul 16. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19615999
-
Sequence and structure of human rhinoviruses reveal the basis of receptor discrimination.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(12):6923-30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.6923-6930.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12768011 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of human rhinovirus serotype 2 (HRV2).J Mol Biol. 2000 Jul 28;300(5):1179-94. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3943. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10903863
-
Review: rhinoviruses and their ICAM receptors.J Struct Biol. 1999 Dec 1;128(1):69-74. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1999.4143. J Struct Biol. 1999. PMID: 10600561 Review.
-
Proposals for the classification of human rhinovirus species C into genotypically assigned types.J Gen Virol. 2010 Oct;91(Pt 10):2409-19. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.023994-0. Epub 2010 Jul 7. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 20610666 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of autophagy does not affect human rhinovirus type 2 production.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(19):10815-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00143-07. Epub 2007 Aug 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17670838 Free PMC article.
-
Human rhinovirus type 2 uncoating at the plasma membrane is not affected by a pH gradient but is affected by the membrane potential.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(8):3778-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01739-08. Epub 2009 Feb 4. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19193784 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses Enter HeLa Cells via Multiple Pathways and Travel to Distinct Intracellular Compartments for Uncoating.Viruses. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):68. doi: 10.3390/v9040068. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28368306 Free PMC article.
-
Small Animal Models of Respiratory Viral Infection Related to Asthma.Viruses. 2018 Dec 1;10(12):682. doi: 10.3390/v10120682. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30513770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site of human rhinovirus RNA uncoating revealed by fluorescent in situ hybridization.J Virol. 2009 Apr;83(8):3770-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00265-08. Epub 2009 Jan 21. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19158243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crump, C. E., E. Arruda, and F. G. Hayden. 1993. In vitro inhibitory activity of soluble ICAM-1 for the numbered serotypes of human rhinovirus. Antiviral Chem. Chemother. 4:323-327.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

