Exon 3 of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early region is required for efficient viral gene expression and for cellular cyclin modulation
- PMID: 15919900
- PMCID: PMC1143685
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7438-7452.2005
Exon 3 of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early region is required for efficient viral gene expression and for cellular cyclin modulation
Abstract
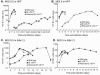
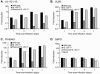
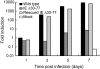
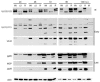
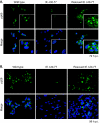
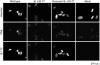
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) major immediate-early (IE) proteins share an 85-amino-acid N-terminal domain specified by exons 2 and 3 of the major IE region, UL122-123. We have constructed IE Delta30-77, a recombinant virus that lacks the majority of IE exon 3 and consequently expresses smaller forms of both IE1 72- and IE2 86-kDa proteins. The mutant virus is viable but growth impaired at both high and low multiplicities of infection and exhibits a kinetic defect that is not rescued by growth in fibroblasts expressing IE1 72-kDa protein. The kinetics of mutant IE2 protein accumulation in IE Delta30-77 virus-infected cells are approximately normal compared to wild-type virus-infected cells, but the IE Delta30-77 virus is delayed in expression of early viral genes, including UL112-113 and UL44, and does not sustain expression of mutant IE1 protein as the infection progresses. Additionally, cells infected with IE Delta30-77 exhibit altered expression of cellular proteins compared to wild-type HCMV-infected cells. PML is not dispersed but is retained at ND10 sites following infection with IE Delta30-77 mutant virus. While the deletion mutant retains the ability to mediate the stabilization of cyclin B1, cdc6, and geminin in infected cells, its capacity to upregulate the expression of cyclin E has been reduced. These data indicate that the activity of one or both of the HCMV major IE proteins is required in vivo for the modulation of cell cycle proteins observed in cells infected with wild-type HCMV.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection.Virology. 2000 Aug 15;274(1):39-55. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0448. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10936087
-
The human cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113 proteins accumulate in viral DNA replication compartments that initiate from the periphery of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies (PODs or ND10).J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10458-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10458-10471.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559364 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase activity is required at early times for accurate processing and accumulation of the human cytomegalovirus UL122-123 and UL37 immediate-early transcripts and at later times for virus production.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(20):11219-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.11219-11232.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15452241 Free PMC article.
-
Bright and Early: Inhibiting Human Cytomegalovirus by Targeting Major Immediate-Early Gene Expression or Protein Function.Viruses. 2020 Jan 16;12(1):110. doi: 10.3390/v12010110. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31963209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional roles of immediate early proteins encoded by the human cytomegalovirus UL36-38, UL115-119, TRS1/IRS1 and US3 loci.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):350-60. doi: 10.1159/000150506. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130045 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis by the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein is necessary for efficient virus replication.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(8):3872-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3872-3883.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16571804 Free PMC article.
-
Development of cell lines that provide tightly controlled temporal translation of the human cytomegalovirus IE2 proteins for complementation and functional analyses of growth-impaired and nonviable IE2 mutant viruses.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(14):7059-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00675-08. Epub 2008 May 7. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18463148 Free PMC article.
-
Triple lysine and nucleosome-binding motifs of the viral IE19 protein are required for human cytomegalovirus S-phase infections.mBio. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):e0016224. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00162-24. Epub 2024 May 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38695580 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0396-z. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25776080 Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE2 86 and IE2 40 proteins differentially regulate UL84 protein expression posttranscriptionally in the absence of other viral gene products.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5158-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00090-10. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20200242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., E. J. Brignole III, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:4899-4913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., and G. S. Hayward. 2000. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology 274:39-55. - PubMed
-
- Baracchini, E., E. Glezer, K. Fish, R. M. Stenberg, J. A. Nelson, and P. Ghazal. 1992. An isoform variant of the cytomegalovirus immediate-early auto repressor functions as a transcriptional activator. Virology 188:518-529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

