Ikappabeta-related vankyrin genes in the Campoletis sonorensis ichnovirus: temporal and tissue-specific patterns of expression in parasitized Heliothis virescens lepidopteran hosts
- PMID: 15919914
- PMCID: PMC1143682
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7617-7628.2005
Ikappabeta-related vankyrin genes in the Campoletis sonorensis ichnovirus: temporal and tissue-specific patterns of expression in parasitized Heliothis virescens lepidopteran hosts
Abstract
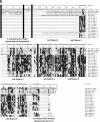
Polydnaviruses (PDVs) are unusual insect viruses that occur in obligate symbiotic associations with parasitic ichneumonid (ichnoviruses, or IVs) and braconid (bracoviruses, or BVs) wasps. PDVs are injected with eggs, ovarian proteins, and venom during parasitization. Following infection of cells in host tissues, viral genes are expressed and their products function to alter lepidopteran host physiology, enabling endoparasitoid development. Here we describe the Campoletis sonorensis IV viral ankyrin (vankyrin) gene family and its transcription. The seven members of this gene family possess ankyrin repeat domains that resemble the inhibitory domains of the Drosophila melanogaster NF-kappabeta transcription factor inhibitor (Ikappabeta) cactus. vankyrin gene expression is detected within 2 to 4 h postparasitization (p.p.) in Heliothis virescens hosts and reaches peak levels by 3 days p.p. Our data indicate that vankyrin genes from the C. sonorensis IV genome are differentially expressed in the tissues of parasitized hosts and can be divided into two subclasses: those that target the host fat body and those that target host hemocytes. Polyclonal antibodies raised against a fat-body targeting vankyrin detected a 19-kDa protein in crude extracts prepared from the 3 days p.p. fat body. Vankyrin-specific Abs localized to 3-day p.p. fat-body and hemocyte nuclei, suggesting a role for vankyrin proteins in the nuclei of C. sonorensis IV-infected cells. These data are evidence for divergent tissue specificities and targeting of multigene families in IVs. We hypothesize that PDV vankyrin genes may suppress NF-kappabeta activity during immune responses and developmental cascades in parasitized lepidopteran hosts of C. sonorensis.
Figures





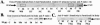

References
-
- Andrade, M. A., C. Perez-Iratxeta, and C. P. Ponting. 2001. Protein repeats: structures, functions, and evolution. J. Struct. Biol. 134:117-131. - PubMed
-
- Asgari, S., M. Hellers, and O. Schmidt. 1996. Host haemocyte inactivation by an insect parasitoid: transient expression of a polydnavirus gene. J. Gen. Virol. 77:2653-2662. - PubMed
-
- Beck, M., and M. R. Strand. 2003. RNA interference silences Microplitis demolitor bracovirus genes and implicates glc1.8 in disruption of adhesion in infected host cells. Virology 314:521-535. - PubMed
-
- Beg, A. A., and A. S. Baldwin, Jr. 1993. The IκB proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Genes Dev. 7:2064-2070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

