Hepatitis C virus core protein suppresses NF-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by direct interaction with IkappaB kinase beta
- PMID: 15919917
- PMCID: PMC1143634
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7648-7657.2005
Hepatitis C virus core protein suppresses NF-kappaB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by direct interaction with IkappaB kinase beta
Abstract
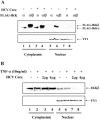
In addition to hepatocytes, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infects immune cells, including macrophages. However, little is known concerning the impact of HCV infection on cellular functions of these immune effector cells. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates IkappaB kinase (IKK) signalsome and NF-kappaB, which leads to the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which catalyzes production of prostaglandins, potent effectors on inflammation and possibly hepatitis. Here, we examined whether expression of HCV core interferes with IKK signalsome activity and COX-2 expression in activated macrophages. In reporter assays, HCV core inhibited NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 and MH-S murine macrophage cell lines treated with bacterial LPS. HCV core inhibited IKK signalsome and IKKbeta kinase activities induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha in HeLa cells and coexpressed IKKgamma in 293 cells, respectively. HCV core was coprecipitated with IKappaKappabeta and prevented nuclear translocation of IKKbeta. NF-kappaB activation by either LPS or overexpression of IKKbeta was sufficient to induce robust expression of COX-2, which was markedly suppressed by ectopic expression of HCV core. Together, these data indicate that HCV core suppresses IKK signalsome activity, which blunts COX-2 expression in macrophages. Additional studies are necessary to determine whether interrupted COX-2 expression by HCV core contributes to HCV pathogenesis.
Figures
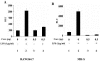
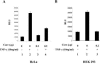
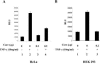






Similar articles
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein activates nuclear factor kappa B-dependent signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):16399-405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006671200. Epub 2001 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278312
-
Additive activation of hepatic NF-kappaB by ethanol and hepatitis B protein X (HBX) or HCV core protein: involvement of TNF-alpha receptor 1-independent and -dependent mechanisms.FASEB J. 2001 Nov;15(13):2551-3. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0217. Epub 2001 Sep 17. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11641261
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Tanshinone IIA inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells: possible involvement of the NIK-IKK, ERK1/2, p38 and JNK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 7;542(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.044. Epub 2006 May 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16797002
-
The effect of reactive oxygen species on the synthesis of prostanoids from arachidonic acid.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;64(4):409-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24101387 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 3 by hepatitis C virus core protein.J Virol. 2013 May;87(10):5718-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03353-12. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23487458 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Hepatocarcinogenesis Following Sustained Virological Response in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Viruses. 2018 Sep 28;10(10):531. doi: 10.3390/v10100531. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30274202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;12(3):641. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030641. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From viruses to cancer: exploring the role of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protein in carcinogenesis.Infect Agent Cancer. 2024 Aug 27;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13027-024-00606-2. Infect Agent Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39192306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein modulates interferon-β production by inhibiting IRF3 activation in immortalized porcine alveolar macrophages.Arch Virol. 2011 Dec;156(12):2187-95. doi: 10.1007/s00705-011-1116-7. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Arch Virol. 2011. PMID: 21947566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter, M. J. 1997. Epidemiology of hepatitis C. Hepatology 26:62S-65S. - PubMed
-
- Alter, M. J., H. S. Margolis, K. Krawczynski, F. N. Judson, A. Mares, W. J. Alexander, P. Y. Hu, J. K. Miller, M. A. Gerber, R. E. Sampliner, E. L. Meeks, M. J. Beach, et al. 1992. The natural history of community-acquired hepatitis C in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 327:1899-1905. - PubMed
-
- Andreone, P., A. Gramenzi, C. Cursaro, M. Biselli, S. Lorenzini, E. Loggi, F. Felline, S. Fiorino, L. Di Giammarino, F. Porzio, S. Galli, and M. Bernardi. 2003. Interferon-alpha combined with ketoprofen as treatment of naive patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized controlled trial. J. Viral Hepat. 10:306-309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

