Role of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in immune response to influenza virus infection in mice
- PMID: 15919918
- PMCID: PMC1143624
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7658-7663.2005
Role of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in immune response to influenza virus infection in mice
Abstract
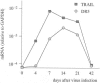
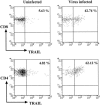
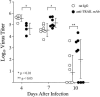
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces apoptosis of various tumor cells but not normal cells. However, various cytokines and virus infection differentially regulate TRAIL and TRAIL receptor expression. It has been demonstrated that virus infection changes the pattern of human TRAIL-receptor expression on normal cells, which were resistant to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, and makes them susceptible to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Since previous studies on the function of TRAIL have been performed mainly in vitro, its physiological role in the immune response to virus infection remains unknown. In the present study, we investigated the expression of TRAIL in the lungs of influenza virus-infected mice and the function of TRAIL in the immune response to infection. Influenza virus infection increased TRAIL mRNA expression in the lung. TRAIL protein expression was induced on NK cells in the lung 4 days after infection. At 7 days after infection, TRAIL protein expression was also detected on CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. However, NK cells and T cells in the lungs of uninfected mice did not express a detectable level of TRAIL on their cell surfaces. DR5, which is a mouse TRAIL receptor, was also induced to express after virus infection. Expression of both TRAIL and DR5 mRNAs was reduced to normal level at 6 weeks after virus infection. Administration of anti-TRAIL monoclonal antibody, which blocks TRAIL without killing TRAIL-expressing cells, to mice during influenza virus infection significantly delayed virus clearance in the lung. These results suggest that TRAIL plays an important role in the immune response to virus infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and function of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand on murine activated NK cells.J Immunol. 1999 Aug 15;163(4):1906-13. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10438925
-
Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptors in viral hepatic diseases.Hum Pathol. 2005 Oct;36(10):1066-73. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2005.07.019. Hum Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16226105
-
Murine TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand) expression induced by T cell activation is blocked by rapamycin, cyclosporin A, and inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, protein kinase C, and protein tyrosine kinases: evidence for TRAIL induction via the T cell receptor signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Oct 10;252(1):96-103. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4631. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10502402
-
Are blockers of gp120/CD4 interaction effective inhibitors of HIV-1 immunopathogenesis?AIDS Rev. 2006 Jan-Mar;8(1):3-8. AIDS Rev. 2006. PMID: 16736946 Review.
-
TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors.Oncogene. 2003 Nov 24;22(53):8628-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207232. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14634624 Review.
Cited by
-
TRAIL: not just for tumors anymore?J Exp Med. 2012 Oct 22;209(11):1903-6. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122235. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 23091198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza-induced expression of functional tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Hum Immunol. 2008 Oct;69(10):634-46. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.07.012. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Hum Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18723061 Free PMC article.
-
The TRAIL to viral pathogenesis: the good, the bad and the ugly.Curr Mol Med. 2009 May;9(4):495-505. doi: 10.2174/156652409788167078. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19519406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hallmarks of CD4 T cell immunity against influenza.J Intern Med. 2011 May;269(5):507-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2011.02367.x. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21362069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine storm and translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments for COVID-19.Front Med. 2023 Dec;17(6):1080-1095. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1044-4. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 38157195 Review.
References
-
- Ashkenazi, A., and V. M. Dixit. 1998. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305-1308. - PubMed
-
- Degli-Esposti, M. A., W. C. Dougall, P. J. Smolak, J. Y. Waugh, C. A. Smith, and R. G. Goodwin. 1997. The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 7:813-820. - PubMed
-
- Gresser, I. 1997. Wherefore interferon? J. Leukoc. Biol. 61:567-574. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

