Identification of the rabies virus alpha/beta interferon antagonist: phosphoprotein P interferes with phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3
- PMID: 15919920
- PMCID: PMC1143667
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7673-7681.2005
Identification of the rabies virus alpha/beta interferon antagonist: phosphoprotein P interferes with phosphorylation of interferon regulatory factor 3
Abstract
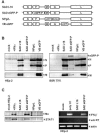
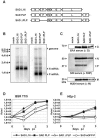
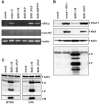
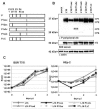
Rabies virus (RV) of the Rhabdoviridae family grows in alpha/beta interferon (IFN)-competent cells, suggesting the existence of viral mechanisms preventing IFN gene expression. We here identify the viral phosphoprotein P as the responsible IFN antagonist. The critical involvement of P was first suggested by the observation that an RV expressing an enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)-P fusion protein (SAD eGFP-P) (S. Finke, K. Brzozka, and K. K. Conzelmann, J. Virol. 78:12333-12343, 2004) was eliminated in IFN-competent HEp-2 cell cultures, in contrast to wild-type (wt) RV or an RV replicon lacking the genes for matrix protein and glycoprotein. SAD eGFP-P induced transcription of the IFN-beta gene and expression of the IFN-responsive MxA and STAT-1 genes. Similarly, an RV expressing low levels of P, which was generated by moving the P gene to a promoter-distal gene position (SAD DeltaPLP), lost the ability to prevent IFN induction. The analysis of RV mutants lacking expression of truncated P proteins P2, P3, or P4, which are expressed from internal AUG codons of the wt RV P open reading frame, further showed that full-length P is competent in suppressing IFN-beta gene expression. In contrast to wt RV, the IFN-inducing SAD DeltaPLP caused S386 phosphorylation, dimerization, and transcriptional activity of IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3). Phosphorylation of IRF-3 by TANK-binding kinase-1 expressed from transfected plasmids was abolished in wt RV-infected cells or by cotransfection of P-encoding plasmids. Thus, RV P is necessary and sufficient to prevent a critical IFN response in virus-infected cells by targeting activation of IRF-3 by an upstream kinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of interferon signaling by rabies virus phosphoprotein P: activation-dependent binding of STAT1 and STAT2.J Virol. 2006 Mar;80(6):2675-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.2675-2683.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16501077 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of interferon-antagonistic functions of rabies virus phosphoprotein: inhibition of interferon regulatory factor 3 activation is important for pathogenicity.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(2):842-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01427-10. Epub 2010 Nov 17. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21084487 Free PMC article.
-
Viral targeting of the interferon-{beta}-inducing Traf family member-associated NF-{kappa}B activator (TANK)-binding kinase-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 20;102(38):13640-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502883102. Epub 2005 Sep 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16155125 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of IRF in host defense.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 Jan;22(1):59-71. doi: 10.1089/107999002753452665. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 11846976 Review.
-
Triggering the interferon response: the role of IRF-3 transcription factor.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999 Jan;19(1):1-13. doi: 10.1089/107999099314360. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999. PMID: 10048763 Review.
Cited by
-
Development in Immunoprophylaxis against Rabies for Animals and Humans.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010 Jan;2(1):3-21. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 23407587 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Innate Immune Inhibition by Non-Segmented Negative-Sense RNA Viruses.J Mol Biol. 2016 Aug 28;428(17):3467-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Jul 31. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27487481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of innate immune responses by rabies virus.Animal Model Exp Med. 2022 Oct;5(5):418-429. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12273. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Animal Model Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36138548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance to rabies virus infection conferred by the PMLIV isoform.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(20):10719-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01286-10. Epub 2010 Aug 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20702643 Free PMC article.
-
Role of interferon antagonist activity of rabies virus phosphoprotein in viral pathogenicity.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(13):6699-710. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00011-10. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20427527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed, M., M. O. McKenzie, S. Puckett, M. Hojnacki, L. Poliquin, and D. S. Lyles. 2003. Ability of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus to suppress beta interferon gene expression is genetically correlated with the inhibition of host RNA and protein synthesis. J. Virol. 77:4646-4657. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499-511. - PubMed
-
- Basler, C. F., and A. Garcia-Sastre. 2002. Viruses and the type I interferon antiviral system: induction and evasion. Int. Rev. Immunol. 21:305-337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

