The structure of the poliovirus 135S cell entry intermediate at 10-angstrom resolution reveals the location of an externalized polypeptide that binds to membranes
- PMID: 15919927
- PMCID: PMC1143686
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7745-7755.2005
The structure of the poliovirus 135S cell entry intermediate at 10-angstrom resolution reveals the location of an externalized polypeptide that binds to membranes
Abstract
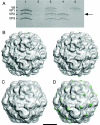
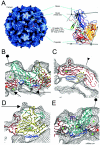
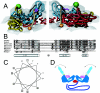
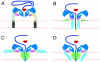
Poliovirus provides a well-characterized system for understanding how nonenveloped viruses enter and infect cells. Upon binding its receptor, poliovirus undergoes an irreversible conformational change to the 135S cell entry intermediate. This transition involves shifts of the capsid protein beta barrels, accompanied by the externalization of VP4 and the N terminus of VP1. Both polypeptides associate with membranes and are postulated to facilitate entry by forming a translocation pore for the viral RNA. We have calculated cryo-electron microscopic reconstructions of 135S particles that permit accurate placement of the beta barrels, loops, and terminal extensions of the capsid proteins. The reconstructions and resulting models indicate that each N terminus of VP1 exits the capsid though an opening in the interface between VP1 and VP3 at the base of the canyon that surrounds the fivefold axis. Comparison with reconstructions of 135S particles in which the first 31 residues of VP1 were proteolytically removed revealed that the externalized N terminus is located near the tips of propeller-like features surrounding the threefold axes rather than at the fivefold axes, as had been proposed in previous models. These observations have forced a reexamination of current models for the role of the 135S particle in transmembrane pore formation and suggest testable alternatives.
Figures


References
-
- Baker, T. S., and R. H. Cheng. 1996. A model-based approach for determining orientations of biological macromolecules imaged by cryoelectron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 116:120-130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

