Involvement of the C-terminal disulfide-bonded loop of murine leukemia virus SU protein in a postbinding step critical for viral entry
- PMID: 15919941
- PMCID: PMC1143666
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7868-7876.2005
Involvement of the C-terminal disulfide-bonded loop of murine leukemia virus SU protein in a postbinding step critical for viral entry
Abstract
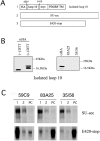
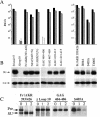
A role for the C-terminal domain (CTD) of murine leukemia virus (MuLV) Env protein in viral fusion was indicated by the potent inhibition of MuLV-induced fusion, but not receptor binding, by two rat monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) specific for epitopes in the CTD. Although these two MAbs, 35/56 and 83A25, have very different patterns of reactivity with viral isolates, determinants of both epitopes were mapped to the last C-terminal disulfide-bonded loop of SU (loop 10), and residues in this loop responsible for the different specificities of these MAbs were identified. Both MAbs reacted with a minor fraction of a truncated SU fragment terminating four residues after loop 10, indicating that while the deleted C-terminal residues were not part of these epitopes, they promoted their formation. Neither MAb recognized the loop 10 region expressed in isolated form, suggesting that these epitopes were not completely localized within loop 10 but required additional sequences located N terminal to the loop. Direct support for a role for loop 10 in fusion was provided by the demonstration that Env mutants containing an extra serine or threonine residue between the second and third positions of the loop were highly attenuated for infectivity and defective in fusion assays, despite wild-type levels of expression, processing, and receptor binding. Other mutations at positions 1 to 3 of loop 10 inhibited processing of the gPr80 precursor protein or led to increased shedding of SU, suggesting that loop 10 also affects Env folding and the stability of the interaction between SU and TM.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct mechanisms of neutralization by monoclonal antibodies specific for sites in the N-terminal or C-terminal domain of murine leukemia virus SU.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):3993-4003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.7.3993-4003.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12634359 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of membrane fusion by murine leukemia viruses is controlled in cis or in trans by interactions between the receptor-binding domain and a conserved disulfide loop of the carboxy terminus of the surface glycoprotein.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3685-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3685-3695.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264358 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of the naturally occurring soluble surface glycoprotein of ecotropic murine leukemia virus: binding specificity and possible conformational change after binding to receptor.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(4):1815-26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1815-1826.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10644355 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of R peptide of murine leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins in syncytium formation and entry.Arch Virol. 2007;152(12):2169-82. doi: 10.1007/s00705-007-1054-6. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Arch Virol. 2007. PMID: 17851730
-
Mutations in the cytoplasmic tail of murine leukemia virus envelope protein suppress fusion inhibition by R peptide.J Virol. 2001 Mar;75(5):2337-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2337-2344.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160737 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Removal of either N-glycan site from the envelope receptor binding domain of Moloney and Friend but not AKV mouse ecotropic gammaretroviruses alters receptor usage.Virology. 2009 Sep 1;391(2):232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.06.015. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19584017 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally Occurring Polymorphisms of the Mouse Gammaretrovirus Receptors CAT-1 and XPR1 Alter Virus Tropism and Pathogenicity.Adv Virol. 2011;2011:975801. doi: 10.1155/2011/975801. Epub 2011 Oct 23. Adv Virol. 2011. PMID: 22312361 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of two monoclonal antibodies reactive with envelope proteins of murine retroviruses: one pan specific antibody and one specific for Moloney leukemia virus.J Virol Methods. 2014 May;200:47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Virol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24556162 Free PMC article.
-
Furin cleavage of the Moloney murine leukemia virus Env precursor reorganizes the spike structure.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 22;111(16):6034-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317972111. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24711391 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of residues outside of the receptor binding domain that influence the infectivity and tropism of porcine endogenous retrovirus.J Virol. 2008 Aug;82(15):7483-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00295-08. Epub 2008 May 28. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18508891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albritton, L. M., L. Tseng, D. Scadden, and J. M. Cunningham. 1989. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell 57:659-666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

