Development of functional human blood and immune systems in NOD/SCID/IL2 receptor {gamma} chain(null) mice
- PMID: 15920010
- PMCID: PMC1895228
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0516
Development of functional human blood and immune systems in NOD/SCID/IL2 receptor {gamma} chain(null) mice
Abstract
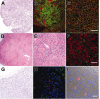
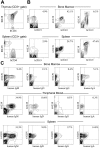
Here we report that a new nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mouse line harboring a complete null mutation of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain (NOD/SCID/interleukin 2 receptor [IL2r] gamma(null)) efficiently supports development of functional human hemato-lymphopoiesis. Purified human (h) CD34(+) or hCD34(+)hCD38(-) cord blood (CB) cells were transplanted into NOD/SCID/IL2rgamma(null) newborns via a facial vein. In all recipients injected with 10(5) hCD34(+) or 2 x 10(4) hCD34(+)hCD38(-) CB cells, human hematopoietic cells were reconstituted at approximately 70% of chimerisms. A high percentage of the human hematopoietic cell chimerism persisted for more than 24 weeks after transplantation, and hCD34(+) bone marrow grafts of primary recipients could reconstitute hematopoiesis in secondary NOD/SCID/IL2rgamma(null) recipients, suggesting that this system can support self-renewal of human hematopoietic stem cells. hCD34(+)hCD38(-) CB cells differentiated into mature blood cells, including myelomonocytes, dendritic cells, erythrocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes. Differentiation into each lineage occurred via developmental intermediates such as common lymphoid progenitors and common myeloid progenitors, recapitulating the steady-state human hematopoiesis. B cells underwent normal class switching, and produced antigen-specific immunoglobulins (Igs). T cells displayed the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-dependent cytotoxic function. Furthermore, human IgA-secreting B cells were found in the intestinal mucosa, suggesting reconstitution of human mucosal immunity. Thus, the NOD/SCID/IL2rgamma(null) newborn system might be an important experimental model to study the human hemato-lymphoid system.
Figures
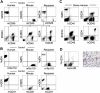
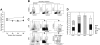

 ) by ELISA. Sera of 3 nonimmunized NOD/SCID/IL2rγnull recipients were used as controls. O.D. indicates optical density. (B) Cytotoxic activity of human T cells generated in NOD/SCID/IL2rg-null mice. hCD4+ and hCD8+ T-cell clones derived from the recipient spleen were cocultured with allogeneic target cells (TAK-LCLs). KIN-LCLs that do not share any HLA type with effector cells or TAK-LCLs (X) were used as negative controls. Both hCD4+ and hCD8+ T-cell lines displayed cytotoxic activity against TAK-LCL in a dose-dependent manner. In hCD4+ T-cell clones, this effect was blocked by anti–HLA-DR antibodies (▴), whereas in hCD8+ T-cell clones, the effect was blocked by anti–HLA class I antibodies (▪). ♦ indicates cytotoxic response to TAK-LCLs without addition of antibodies.
) by ELISA. Sera of 3 nonimmunized NOD/SCID/IL2rγnull recipients were used as controls. O.D. indicates optical density. (B) Cytotoxic activity of human T cells generated in NOD/SCID/IL2rg-null mice. hCD4+ and hCD8+ T-cell clones derived from the recipient spleen were cocultured with allogeneic target cells (TAK-LCLs). KIN-LCLs that do not share any HLA type with effector cells or TAK-LCLs (X) were used as negative controls. Both hCD4+ and hCD8+ T-cell lines displayed cytotoxic activity against TAK-LCL in a dose-dependent manner. In hCD4+ T-cell clones, this effect was blocked by anti–HLA-DR antibodies (▴), whereas in hCD8+ T-cell clones, the effect was blocked by anti–HLA class I antibodies (▪). ♦ indicates cytotoxic response to TAK-LCLs without addition of antibodies.References
-
- Greiner DL, Hesselton RA, Shultz LD. SCID mouse models of human stem cell engraftment. Stem Cells. 1998;16: 166-177. - PubMed
-
- McCune JM, Namikawa R, Kaneshima H, Shultz LD, Lieberman M, Weissman IL. The SCID-hu mouse: murine model for the analysis of human hematolymphoid differentiation and function. Science. 1988;241: 1632-1639. - PubMed
-
- Mosier DE, Gulizia RJ, Baird SM, Wilson DB. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988;335: 256-259. - PubMed
-
- Kaneshima H, Namikawa R, McCune JM. Human hematolymphoid cells in SCID mice. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994;6: 327-333. - PubMed
-
- Pflumio F, Izac B, Katz A, Shultz LD, Vainchenker W, Coulombel L. Phenotype and function of human hematopoietic cells engrafting immune-deficient CB17-severe combined immunodeficiency mice and nonobese diabetic-severe combined immunodeficiency mice after transplantation of human cord blood mononuclear cells. Blood. 1996;88: 3731-3740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

