Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo
- PMID: 15920154
- PMCID: PMC1602424
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62479-0
Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo
Abstract
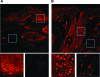
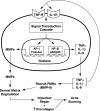
Acne is the most common skin disease, causing significant psychosocial problems for those afflicted. Currently available agents for acne treatment, such as oral antibiotics and isotretinoin (Accutane), have limited use. Thus, development of novel agents to treat this disease is needed. However, the pathophysiology of acne inflammation is poorly understood. Before new therapeutic strategies can be devised, knowledge regarding molecular mechanisms of acne inflammation is required. We report here that transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 are activated in acne lesions with consequent elevated expression of their target gene products, inflammatory cytokines and matrix-degrading metalloproteinases, respectively. These elevated gene products are molecular mediators of inflammation and collagen degradation in acne lesions in vivo. This new knowledge enables a rational strategy for development of pharmacological agents that can target the inflammation and matrix remodeling that occurs in severe acne.
Figures





References
-
- Brown S, Shalita A. Acne vulgaris. Lancet. 1998;351:1871–1876. - PubMed
-
- Kraning K, Odland G. Prevalence, morbidity, and cost of dermatological diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 1979;73:395–401. - PubMed
-
- Koo J, Smith L. Psychologic aspects of acne. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Knutson D. Ultrastructural observations in acne vulgaris: the normal sebaceous follicle and acne lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1974;62:288–307. - PubMed
-
- Lavker R, Leyden J. Lamellar inclusions in follicular horny cells: a new aspect of abnormal keratinization. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979;69:362–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

