Prevention of neutrophil extravasation by hepatocyte growth factor leads to attenuations of tubular apoptosis and renal dysfunction in mouse ischemic kidneys
- PMID: 15920173
- PMCID: PMC1602426
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62498-4
Prevention of neutrophil extravasation by hepatocyte growth factor leads to attenuations of tubular apoptosis and renal dysfunction in mouse ischemic kidneys
Abstract
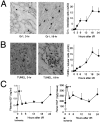
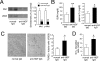
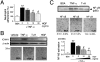
Ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injuries occur in numerous organs under pathophysiological conditions. In this process, neutrophils play important roles in eliciting parenchymal injuries. Using a murine model of renal I/R, we show that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a natural ligand that inhibits endothelial injuries and neutrophil extravasation. In mice after renal I/R, plasma HGF levels increased, along with c-Met/HGF receptor phosphorylation in the vascular endothelium. However, this c-Met activation was transient, associated with a decrease in endogenous HGF level, and followed by neutrophil infiltration and renal dysfunction. Suppression of endothelial c-Met phosphorylation by anti-HGF IgG led to rapid progressions of neutrophil extravasation, tubular apoptosis, and renal dysfunction. Inversely, enhancement of the c-Met activation by exogenous HGF blocked endothelial/tubular apoptotic injuries and acute renal failure. In this process, HGF prevented endothelial nuclear factor kappaB activation and inhibited induction of an adhesion molecule (ICAM-1), resulting in attenuated vascular edema and neutrophil infiltration. Thus, we conclude that 1) the HGF/c-Met system of endothelial cells confers an initial barrier to block neutrophil infiltration, and 2) transient and insufficient HGF production allows manifestation of postischemic renal failure. Our study provides a rationale for why HGF supplementation elicits therapeutic effects in ischemic kidneys.
Figures

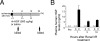


References
-
- Beekhuizen H, van-de Gevel JS. Endothelial cell adhesion molecules in inflammation and postischemic reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 1998;30:4251–4256. - PubMed
-
- Jordan JE, Zhao ZQ, Vinten-Johansen J. The role of neutrophils in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;43:860–878. - PubMed
-
- Lauriat S, Linas SL. The role of neutrophils in acute renal failure. Semin Nephrol. 1998;18:498–504. - PubMed
-
- Scarabelli T, Stephanou A, Rayment N, Pasini E, Comini L, Curello S, Ferrari R, Latchman D. Apoptosis of endothelial cells precedes myocyte cell apoptosis in ischemia and reperfusion injury. Circulation. 2001;104:253–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

