Movements of the epsilon-subunit during catalysis and activation in single membrane-bound H(+)-ATP synthase
- PMID: 15920483
- PMCID: PMC1150879
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600682
Movements of the epsilon-subunit during catalysis and activation in single membrane-bound H(+)-ATP synthase
Abstract
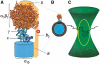
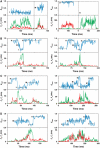
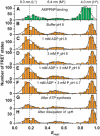
F0F1-ATP synthases catalyze proton transport-coupled ATP synthesis in bacteria, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. In these complexes, the epsilon-subunit is involved in the catalytic reaction and the activation of the enzyme. Fluorescence-labeled F0F1 from Escherichia coli was incorporated into liposomes. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) revealed that the epsilon-subunit rotates stepwise showing three distinct distances to the b-subunits in the peripheral stalk. Rotation occurred in opposite directions during ATP synthesis and hydrolysis. Analysis of the dwell times of each FRET state revealed different reactivities of the three catalytic sites that depended on the relative orientation of epsilon during rotation. Proton transport through the enzyme in the absence of nucleotides led to conformational changes of epsilon. When the enzyme was inactive (i.e. in the absence of substrates or without membrane energization), three distances were found again, which differed from those of the active enzyme. The three states of the inactive enzyme were unequally populated. We conclude that the active-inactive transition was associated with a conformational change of epsilon within the central stalk.
Figures




References
-
- Aggeler R, Capaldi RA (1992) Cross-linking of the γ subunit of the Escherichia coli ATPase (ECF1) via cysteines introduced by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 267: 21355–21359 - PubMed
-
- Aggeler R, Ogilvie I, Capaldi RA (1997) Rotation of a γ–ɛ subunit domain in the Escherichia coli F1F0-ATP synthase complex. The γ–ɛ subunits are essentially randomly distributed relative to the α3β3δ domain in the intact complex. J Biol Chem 272: 19621–19624 - PubMed
-
- Boldt F-M, Heinze J, Diez M, Petersen J, Börsch M (2004) Real-time pH microscopy down to the molecular level by combined scanning electrochemical microscopy/single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy. Anal Chem 76: 3473–3481 - PubMed
-
- Börsch M, Diez M, Zimmermann B, Reuter R, Gräber P (2002) Stepwise rotation of the γ-subunit of EF0F1-ATP synthase observed by intramolecular single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. FEBS Lett 527: 147–152 - PubMed
-
- Börsch M, Turina P, Eggeling C, Fries JR, Seidel CA, Labahn A, Gräber P (1998) Conformational changes of the H+-ATPase from Escherichia coli upon nucleotide binding detected by single molecule fluorescence. FEBS Lett 437: 251–254 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

