EEDA: a protein associated with an early stage of stratified epithelial differentiation
- PMID: 15920738
- PMCID: PMC1523255
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.20433
EEDA: a protein associated with an early stage of stratified epithelial differentiation
Abstract
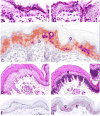
Using suppressive subtractive hybridization, we have identified a novel gene, which we named early epithelial differentiation associated (EEDA), which is uniquely associated with an early stage of stratified epithelial differentiation. In epidermis, esophageal epithelium, and tongue epithelium, EEDA mRNA, and antigen was abundant in suprabasal cells, but was barely detectable in more differentiated cells. Consistent with the limbal location of corneal epithelial stem cells, EEDA was expressed in basal corneal epithelial cells that are out of the stem cell compartment, as well as the suprabasal corneal epithelial cells. The strongest EEDA expression occurred in suprabasal precortical cells of mouse, bovine, and human anagen follicles. Developmental studies showed that the appearance of EEDA in embryonic mouse epidermis (E 15.5) coincided with morphological keratinization. Interestingly, EEDA expression is turned off when epithelia were perturbed by wounding and by cultivation under both low and high Ca2+ conditions. Our results indicate that EEDA is involved in the early stages of normal epithelial differentiation, and that EEDA is important for the "normal" differentiation pathway in a wide range of stratified epithelia.
Copyright 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures











References
-
- Asselineau D, Bernard BA, Bailly C, Darmon M, Prunieras M. Human epidermis reconstructed by culture: is it "normal"? J Invest Dermatol. 1986;86(2):181–186. - PubMed
-
- Cabodi S, Calautti E, Talora C, Kuroki T, Stein PL, Dotto GP. A PKC-eta/Fyn-dependent pathway leading to keratinocyte growth arrest and differentiation. Mol Cell. 2000;6(5):1121–1129. - PubMed
-
- Chaloin-Dufau C, Sun T-T, Dhouailly D. Appearance of the keratin pair K3/K12 during embryonic and adult corneal epithelial differentiation in the chick and in the rabbit. Cell Diff Dev. 1990;32:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Chen WY, Mui MM, Kao WW, Liu CY, Tseng SC. Conjunctival epithelial cells do not transdifferentiate in organotypic cultures: expression of K12 keratin is restricted to corneal epithelium. Current Eye Research. 1994;13(10):765–778. - PubMed
-
- Cotsarelis G, Cheng SZ, Dong G, Sun TT, Lavker RM. Existence of slow-cycling limbal epithelial basal cells that can be preferentially stimulated to proliferate: implications on epithelial stem cells. Cell. 1989;57(2):201–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

