An expression screen reveals modulators of class II histone deacetylase phosphorylation
- PMID: 15923258
- PMCID: PMC1149448
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503275102
An expression screen reveals modulators of class II histone deacetylase phosphorylation
Abstract
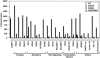
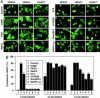
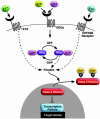
Class II histone deacetylases (HDACs) repress transcription by associating with a variety of transcription factors and corepressors. Phosphorylation of a set of conserved serine residues in the N-terminal extensions of class II HDACs creates binding sites for 14-3-3 chaperone proteins, which trigger nuclear export of these HDACs, thereby derepressing specific target genes in a signal-dependent manner. To identify intracellular signaling pathways that control phosphorylation of HDAC5, a class II HDAC, we designed a eukaryotic cDNA expression screen in which a GAL4-dependent luciferase reporter was expressed with the DNA-binding domain of GAL4 fused to the N-terminal extension of HDAC5 and the VP16 transcription activation domain fused to 14-3-3. The transfection of COS cells with cDNA expression libraries results in activation of luciferase expression by cDNAs encoding HDAC5 kinases or modulators of such kinases that enable phosphorylated GAL4-HDAC5 to recruit 14-3-3-VP16 with consequent reconstitution of a functional transcriptional complex. Our results reveal a remarkable variety of signaling pathways that converge on the signal-responsive phosphorylation sites in HDAC5, thereby enabling HDAC5 to connect extracellular signals to the genome.
Figures

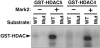
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

