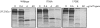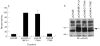Genetic, functional, and histopathological evaluation of two C-terminal BRCA1 missense variants
- PMID: 15923272
- PMCID: PMC2564506
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2005.033258
Genetic, functional, and histopathological evaluation of two C-terminal BRCA1 missense variants
Abstract
Background: The vast majority of BRCA1 missense sequence variants remain uncharacterized for their possible effect on protein expression and function, and therefore are unclassified in terms of their pathogenicity. BRCA1 plays diverse cellular roles and it is unlikely that any single functional assay will accurately reflect the total cellular implications of missense mutations in this gene.
Objective: To elucidate the effect of two BRCA1 variants, 5236G>C (G1706A) and 5242C>A (A1708E) on BRCA1 function, and to survey the relative usefulness of several assays to direct the characterisation of other unclassified variants in BRCA genes.
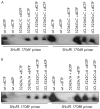
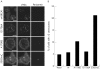
Methods and results: Data from a range of bioinformatic, genetic, and histopathological analyses, and in vitro functional assays indicated that the 1708E variant was associated with the disruption of different cellular functions of BRCA1. In transient transfection experiments in T47D and 293T cells, the 1708E product was mislocalised to the cytoplasm and induced centrosome amplification in 293T cells. The 1708E variant also failed to transactivate transcription of reporter constructs in mammalian transcriptional transactivation assays. In contrast, the 1706A variant displayed a phenotype comparable to wildtype BRCA1 in these assays. Consistent with functional data, tumours from 1708E carriers showed typical BRCA1 pathology, while tumour material from 1706A carriers displayed few histopathological features associated with BRCA1 related tumours.
Conclusions: A comprehensive range of genetic, bioinformatic, and functional analyses have been combined for the characterisation of BRCA1 unclassified sequence variants. Consistent with the functional analyses, the combined odds of causality calculated for the 1706A variant after multifactorial likelihood analysis (1:142) indicates a definitive classification of this variant as "benign". In contrast, functional assays of the 1708E variant indicate that it is pathogenic, possibly through subcellular mislocalisation. However, the combined odds of 262:1 in favour of causality of this variant does not meet the minimal ratio of 1000:1 for classification as pathogenic, and A1708E remains formally designated as unclassified. Our findings highlight the importance of comprehensive genetic information, together with detailed functional analysis for the definitive categorisation of unclassified sequence variants. This combination of analyses may have direct application to the characterisation of other unclassified variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
References
-
- Duan J, Wainwright M S, Comeron J M, Saitou N, Sanders A R, Gelernter J, Gejman P V. Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum Mol Genet 200312(3)205–216. - PubMed
-
- Vega A, Campos B, Bressac‐De‐Paillerets B, Bond P M, Janin N, Douglas F S, Domenech M, Baena M, Pericay C, Alonso C, Carracedo A, Baiget M, Diez O. The R71G BRCA1 is a founder Spanish mutation and leads to aberrant splicing of the transcript. Hum Mutat 200117(6)520–521. - PubMed
-
- Hofstra R M, Mulder I M, Vossen R, de Koning‐Gans P A, Kraak M, Ginjaar I B, van der Hout A H, Bakker E, Buys C H, van Ommen G J, van Essen A J, den Dunnen J T. DGGE‐based whole‐gene mutation scanning of the dystrophin gene in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. Hum Mutat 200423(1)57–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous