Positive and negative factors confer phase-specific circadian regulation of transcription in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15923346
- PMCID: PMC1167542
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.033035
Positive and negative factors confer phase-specific circadian regulation of transcription in Arabidopsis
Abstract
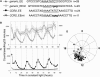
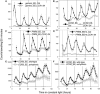
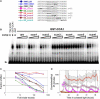
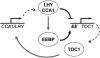
The circadian clock exerts a major influence on transcriptional regulation in plants and other organisms. We have previously identified a motif called the evening element (EE) that is overrepresented in the promoters of evening-phased genes. Here, we demonstrate that multimerized EEs are necessary and sufficient to confer evening-phased circadian regulation. Although flanking sequences are not required for EE function, they can modulate EE activity. One flanking sequence, taken from the PSEUDORESPONSE REGULATOR 9 promoter, itself confers dawn-phased rhythms and has allowed us to define a new clock promoter motif (the morning element [ME]). Scanning mutagenesis reveals that both activators and repressors of gene expression act through the ME and EE. Although our experiments confirm that CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1) and LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY) are likely to act as repressors via the EE, they also show that they have an unexpected positive effect on EE-mediated gene expression as well. We have identified a clock-regulated activity in plant extracts that binds specifically to the EE and has a phase consistent with it being an activator of expression through the EE. This activity is reduced in CCA1/LHY null plants, suggesting it may itself be part of a circadian feedback loop and perhaps explaining the reduction in EE activity in these double mutant plants.
Figures


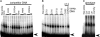
References
-
- Alabadi, D., Oyama, T., Yanovsky, M.J., Harmon, F.G., Mas, P., and Kay, S.A. (2001). Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 293, 880–883. - PubMed
-
- Alabadi, D., Yanovsky, M.J., Mas, P., Harmer, S.L., and Kay, S.A. (2002). Critical role for CCA1 and LHY in maintaining circadian rhythmicity in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 12, 757–761. - PubMed
-
- Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743. - PubMed
-
- Cyran, S.A., Buchsbaum, A.M., Reddy, K.L., Lin, M.C., Glossop, N.R., Hardin, P.E., Young, M.W., Storti, R.V., and Blau, J. (2003). vrille, Pdp1, and dClock form a second feedback loop in the Drosophila circadian clock. Cell 112, 329–341. - PubMed
-
- Darlington, T.K., Lyons, L.C., Hardin, P.E., and Kay, S.A. (2000). The period E-box is sufficient to drive circadian oscillation of transcription in vivo. J. Biol. Rhythms 15, 462–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

