Polarized expression of CD74 by gastric epithelial cells
- PMID: 15923369
- PMCID: PMC3957538
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.4A6552.2005
Polarized expression of CD74 by gastric epithelial cells
Abstract
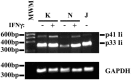
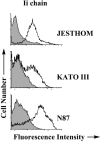
CD74 is known as the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-associated invariant chain (Ii) that regulates the cell biology and functions of MHC class II molecules. Class II MHC and Ii expression was believed to be restricted to classical antigen-presenting cells (APC); however, during inflammation, other cell types, including mucosal epithelial cells, have also been reported to express class II MHC molecules. Given the importance of Ii in the biology of class II MHC, we sought to examine the expression of Ii by gastric epithelial cells (GEC) to determine whether class II MHC molecules in these nonconventional APC cells were under the control of Ii and to further support the role that these cells may play in local immune and inflammatory responses during Helicobacter pylori infection. Thus we examined the expression of Ii on GEC from human biopsy samples and then confirmed this observation using independent methods on several GEC lines. The mRNA for Ii was detected by RT-PCR, and the various protein isoforms were also detected. Interestingly, these cells have a high level expression of surface Ii, which is polarized to the apical surface. These studies are the first to demonstrate the constitutive expression of Ii by human GEC.
Figures





References
-
- Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B. (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61: 1303–1313 - PubMed
-
- Bakke O, Dobberstein B. (1990) MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell 63: 707–716 - PubMed
-
- Bamford KB, Fan X, Crowe SE, Leary JF, Gourley WK, Luthra GK, Brooks EG, et al. (1998) Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology 114: 482–492 - PubMed
-
- Barrera C, Ye G, Espejo R, Gunasena S, Almanza R, Leary J, Crowe S, et al. (2001) Expression of cathepsins B, L, S, and D by gastric epithelial cells implicates them as antigen presenting cells in local immune responses. Hum Immunol 62: 1081–1091 - PubMed
-
- Barrera C, Espejo R, Reyes VE. (2002) Differential glycosylation of MHC class II molecules on gastric epithelial cells: implications in local immune responses. Hum Immunol 63: 384–393 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

