Corneal birefringence changes after laser assisted in situ keratomileusis and their influence on retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement by means of scanning laser polarimetry
- PMID: 15923503
- PMCID: PMC1772677
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2004.054726
Corneal birefringence changes after laser assisted in situ keratomileusis and their influence on retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement by means of scanning laser polarimetry
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate changes in corneal polarisation properties and their influence on peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) thickness measurements after laser assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) by means of scanning laser polarimetry (SLP) with variable corneal polarisation compensator (VCC) in normal white subjects.
Methods: SLP was performed by means of GDx VCC on 32 eyes of 32 normal subjects who underwent LASIK for ametropia correction. Corneal polarisation axis and magnitude and RNFL thickness were measured before and 8 days after LASIK. RNFL thickness data and corneal polarimetric data of one randomly selected eye per subject were analysed by the Wilcoxon signed ranks test. Correlations between corneal ablation depth, corneal polarimetric changes, and RNFL thickness changes were investigated using Spearman's rho test.
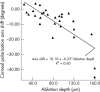
Results: The corneal polarisation axis significantly shifted from 15.1 degrees (17.0 degrees ) to 6.9 degrees (12.9 degrees ) (p = 0.00006) after LASIK and this change showed a strong correlation with corneal ablation depth (rho = -0.7, p = 0.00002). Among GDx parameters, TSNIT, SUP, and SD showed significant changes after LASIK and for SUP and SD these changes were well correlated with the shift in corneal polarisation axis (rho = 0.54, p = 0.03 and rho = 0.45, p = 0.01, respectively). SUP and SD changes were neutralised after compensating for corneal polarimetric changes but not TSNIT changes. NFI, a discriminating parameter, was found to be affected after LASIK only after compensating for corneal polarimetric changes.
Conclusions: LASIK induces a shift in corneal polarisation axis which is responsible for inaccuracies in RNFL thickness measurements. A customised compensation for corneal polarimetric changes after LASIK allows normalisation of some of the thickness parameters except for TSNIT and NFI.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinal nerve fiber layer measurements do not change after LASIK for high myopia as measured by scanning laser polarimetry with custom compensation.Ophthalmology. 2005 Jan;112(1):92-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.07.027. Ophthalmology. 2005. PMID: 15629826
-
Assessment of nerve fiber layer thickness before and after laser in situ keratomileusis using scanning laser polarimetry with variable corneal compensation.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 May;31(5):1035-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.12.045. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 15975475
-
Influence of LASIK on scanning laser polarimetric measurement of the retinal nerve fibre layer with fixed angle and customised corneal polarisation compensation.Br J Ophthalmol. 2003 Oct;87(10):1241-6. doi: 10.1136/bjo.87.10.1241. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003. PMID: 14507758 Free PMC article.
-
Cornea refractive surgery and scanning laser polarimetry.Oftalmologia. 2009;53(4):10-2. Oftalmologia. 2009. PMID: 20361643 Review.
-
Considerations of glaucoma in patients undergoing corneal refractive surgery.Surv Ophthalmol. 2005 May-Jun;50(3):245-51. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2005.02.006. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15850813 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the retinal nerve fiber layer measurements, after photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis, using scanning laser polarimetry (GDX VCC).Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010 May;248(5):731-6. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1273-5. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20072786 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness following mechanical microkeratome-assisted versus femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK.Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:1919-22. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S51774. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24109171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoh ST, Ishikawa H, Greenfield DS, et al. Peripapillary nerve fiber layer thickness measurement reproducibility using scanning laser polarimetry. J Glaucoma 1998;7:12–15. - PubMed
-
- Kook MS, Sung K, Park RH, et al. Reproducibility of scanning laser polarimetry (GDx) of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2001;239:118–21. - PubMed
-
- Weinreb RN, Shakiba S, Zangwill L. Scanning laser polarimetry to measure the nerve fiber layer of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;119:627–36. - PubMed
-
- Knighton RW, Huang X-R. Directional and spectral reflectance of the rat retinal nerve fiber layer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999;40:639–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources