Behavioral correlates of activity in identified hypocretin/orexin neurons
- PMID: 15924864
- PMCID: PMC8281334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.035
Behavioral correlates of activity in identified hypocretin/orexin neurons
Abstract
Micropipette recording with juxtacellular Neurobiotin ejection, linked micropipette-microwire recording, and antidromic and orthodromic activation from the ventral tegmental area and locus coeruleus were used to identify hypocretin (Hcrt) cells in anesthetized rats and develop criteria for identification of these cells in unanesthetized, unrestrained animals. We found that Hcrt cells have broad action potentials with elongated later positive deflections that distinguish them from adjacent antidromically identified cells. They are relatively inactive in quiet waking but are transiently activated during sensory stimulation. Hcrt cells are silent in slow wave sleep and tonic periods of REM sleep, with occasional burst discharge in phasic REM. Hcrt cells discharge in active waking and have moderate and approximately equal levels of activity during grooming and eating and maximal activity during exploratory behavior. Our findings suggest that these cells are activated during emotional and sensorimotor conditions similar to those that trigger cataplexy in narcoleptic animals.
Figures
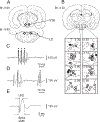
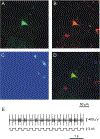
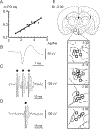
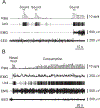

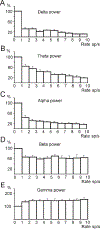
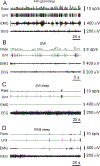
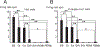
Comment in
-
Hypocretins: waking, arousal, or action?Neuron. 2005 Jun 2;46(5):696-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.016. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15924855 Review.
References
-
- Aston-Jones G, Chiang C, and Alexinsky T (1991). Discharge of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats and monkeys suggests a role in vigilance. Prog. Brain Res. 88, 501–520. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Chen S, Zhu Y, and Oshinsky ML (2001). A neural circuit for circadian regulation of arousal. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 732–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

