Alcoholism is a disinhibitory disorder: neurophysiological evidence from a Go/No-Go task
- PMID: 15925035
- PMCID: PMC3758477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2004.08.004
Alcoholism is a disinhibitory disorder: neurophysiological evidence from a Go/No-Go task
Abstract
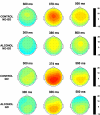
Response inhibition is considered a core dimension in alcoholism and its co-existing disorders. The major objective of this study is to compare the magnitude and spatial distribution of ERP components during response activation and inhibition in alcoholics (N = 30) and normal controls (N = 30) using a visual Go/No-Go task. The results indicate that alcoholics manifest a decreased P3(00) amplitude during Go as well as No-Go conditions. The difference between Go and No-Go processing was more evident in controls than in alcoholics. The topography of current source density in alcoholics during the P3 response was found to be very different from that of normals, suggesting that alcoholics perhaps activated inappropriate brain circuitry during cognitive processing. The significantly reduced No-Go P3 along with the relatively less anteriorized CSD topography during No-Go condition suggests poor inhibitory control in alcoholics. It is proposed that the No-Go P3, the electrophysiological signature of response inhibition, can be considered as an endophenotypic marker in alcoholism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Delta, theta, and alpha event-related oscillations in alcoholics during Go/NoGo task: Neurocognitive deficits in execution, inhibition, and attention processing.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Feb 4;65:158-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.10.002. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26456730 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-anatomical mapping of NoGo-P3 in the offspring of alcoholics: evidence of cognitive and neural disinhibition as a risk for alcoholism.Clin Neurophysiol. 2005 May;116(5):1049-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2004.12.015. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15826845 Free PMC article.
-
P3 Component as a Potential Endophenotype for Control Inhibition in Offspring of Alcoholics.Alcohol Alcohol. 2018 Nov 1;53(6):699-706. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agy051. Alcohol Alcohol. 2018. PMID: 30020398
-
Alcohol-related ERP changes recorded from different modalities: a topographic analysis.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002 Mar;26(3):303-17. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. PMID: 11923582
-
The effects of fetal alcohol syndrome on response execution and inhibition: an event-related potential study.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Nov;33(11):1994-2004. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01038.x. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009. PMID: 19719791
Cited by
-
More widespread and rigid neuronal representation of reward expectation underlies impulsive choices.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 12:2024.04.11.588637. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.11.588637. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38645037 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Atypical response inhibition and error processing in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and schizophrenia: Towards neuromarkers of disease progression and risk.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102351. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102351. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32731196 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Control in Excessive Social Networking Users: Evidence From an Event-Related Potential-Based Go-Nogo Task.Front Psychol. 2019 Aug 7;10:1810. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01810. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31447743 Free PMC article.
-
Distress intolerance modulation of neurophysiological markers of cognitive control during a complex go/no-go task.J Abnorm Psychol. 2018 Jan;127(1):12-29. doi: 10.1037/abn0000323. J Abnorm Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29369665 Free PMC article.
-
Delta, theta, and alpha event-related oscillations in alcoholics during Go/NoGo task: Neurocognitive deficits in execution, inhibition, and attention processing.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Feb 4;65:158-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.10.002. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26456730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almasy L, Porjesz B, Blangero J, Chorlian DB, O’Connor SJ, Kuperman S, Rohrbaugh J, Bauer LO, Reich T, Polich J, Begleiter H. Heritability of event-related brain potentials in families with a history of alcoholism. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1999a;88:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin AP, van Baal GC, van Beijsterveldt CE, de Geus EJ, Grant J, Boomsma DI. Genetic correlation between the P300 event-related brain potential and the EEG power spectrum. Behavior Genetics. 2001;31:545–554. - PubMed
-
- Barkley RA. Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychological Bulletin. 1997;121:65–94. - PubMed
-
- Barkley RA. The executive functions and self-regulation: an evolutionary neuropsychological perspective. Neuropsychology Review. 2001;11:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Bauer LO. CNS recovery from cocaine, cocaine and alcohol, or opioid dependence: a P300 study. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2001;112:1508–1515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

