Triadins are not triad-specific proteins: two new skeletal muscle triadins possibly involved in the architecture of sarcoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 15927957
- PMCID: PMC2739232
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M501484200
Triadins are not triad-specific proteins: two new skeletal muscle triadins possibly involved in the architecture of sarcoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
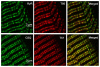
We have cloned two new triadin isoforms from rat skeletal muscle, Trisk 49 and Trisk 32, which were named according to their theoretical molecular masses (49 and 32 kDa, respectively). Specific antibodies directed against each protein were produced to characterize both new triadins. Both are expressed in adult rat skeletal muscle, and their expression in slow twitch muscle is lower than that in fast twitch muscle. Using double immunofluorescent labeling, the localization of these two triadins was studied in comparison to well-characterized proteins such as ryanodine receptor, calsequestrin, desmin, Ca(2+)-ATPase, and titin. None of these two triadins are localized within the rat skeletal muscle triad. Both are instead found in different parts of the longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum. We attempted to identify partners for each isoform: neither is associated with ryanodine receptor; Trisk 49 could be associated with titin or another sarcomeric protein; and Trisk 32 could be associated with IP(3) receptor. These results open further fields of research concerning the functions of these two proteins; in particular, they could be involved in the set up and maintenance of a precise sarcoplasmic reticulum structure.
Figures









References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

