Osteopontin is a hematopoietic stem cell niche component that negatively regulates stem cell pool size
- PMID: 15928197
- PMCID: PMC2213260
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041992
Osteopontin is a hematopoietic stem cell niche component that negatively regulates stem cell pool size
Abstract
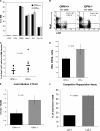
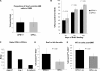
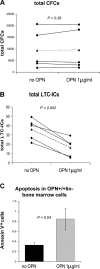
Stem cells reside in a specialized niche that regulates their abundance and fate. Components of the niche have generally been defined in terms of cells and signaling pathways. We define a role for a matrix glycoprotein, osteopontin (OPN), as a constraining factor on hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow microenvironment. Osteoblasts that participate in the niche produce varying amounts of OPN in response to stimulation. Using studies that combine OPN-deficient mice and exogenous OPN, we demonstrate that OPN modifies primitive hematopoietic cell number and function in a stem cell-nonautonomous manner. The OPN-null microenvironment was sufficient to increase the number of stem cells associated with increased stromal Jagged1 and Angiopoietin-1 expression and reduced primitive hematopoietic cell apoptosis. The activation of the stem cell microenvironment with parathyroid hormone induced a superphysiologic increase in stem cells in the absence of OPN. Therefore, OPN is a negative regulatory element of the stem cell niche that limits the size of the stem cell pool and may provide a mechanism for restricting excess stem cell expansion under conditions of niche stimulation.
Figures



References
-
- Kiger, A.A., D.L. Jones, C. Schulz, M.B. Rogers, and M.T. Fuller. 2001. Stem cell self-renewal specified by JAK-STAT activation in response to a support cell cue. Science. 294:2542–2545. - PubMed
-
- Xie, T., and A.C. Spradling. 2000. A niche maintaining germ line stem cells in the Drosophila ovary. Science. 290:328–330. - PubMed
-
- Zhang, J., C. Niu, L. Ye, H. Huang, X. He, W.G. Tong, J. Ross, J. Haug, T. Johnson, J.Q. Feng, et al. 2003. Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature. 425:836–841. - PubMed
-
- Calvi, L.M., G.B. Adams, K.W. Weibrecht, J.M. Weber, D.P. Olson, M.C. Knight, R.P. Martin, E. Schipani, P. Divieti, F.R. Bringhurst, et al. 2003. Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature. 425:841–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

