Class II phosphoinositide 3-kinase defines a novel signaling pathway in cell migration
- PMID: 15928202
- PMCID: PMC2171608
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200408005
Class II phosphoinositide 3-kinase defines a novel signaling pathway in cell migration
Abstract
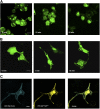
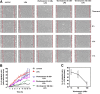
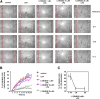
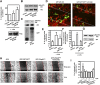
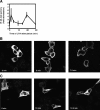
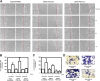
The lipid products of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) are involved in many cellular responses such as proliferation, migration, and survival. Disregulation of PI3K-activated pathways is implicated in different diseases including cancer and diabetes. Among the three classes of PI3Ks, class I is the best characterized, whereas class II has received increasing attention only recently and the precise role of these isoforms is unclear. Similarly, the role of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PtdIns-3-P) as an intracellular second messenger is only just beginning to be appreciated. Here, we show that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) stimulates the production of PtdIns-3-P through activation of a class II PI3K (PI3K-C2beta). Both PtdIns-3-P and PI3K-C2beta are involved in LPA-mediated cell migration. This study is the first identification of PtdIns-3-P and PI3K-C2beta as downstream effectors in LPA signaling and demonstration of an intracellular role for a class II PI3K. Defining this novel PI3K-C2beta-PtdIns-3-P signaling pathway may help clarify the process of cell migration and may shed new light on PI3K-mediated intracellular events.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, N.G., T. Ahmad, K. Chan, R. Dobson, and N.J. Bundred. 2001. ZD1839 (Iressa), a novel epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, potently inhibits the growth of EGFR-positive cancer cell lines with or without erbB2 overexpression. Int. J. Cancer. 94:774–782. - PubMed
-
- Arcaro, A., S. Volinia, M.J. Zvelebil, R. Stein, S.J. Watton, M.J. Layton, I. Gout, K. Ahmadi, J. Downward, and M.D. Waterfield. 1998. Human phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2beta, the role of calcium and the C2 domain in enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 273:33082–33090. - PubMed
-
- Bian, D., S. Su, C. Mahanivong, R.K. Cheng, Q. Han, Z.K. Pan, P. Sun, and S. Huang. 2004. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates ovarian cancer cell migration via a Ras-MEK Kinase 1 pathway. Cancer Res. 64:4209–4217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

