RNA chaperone activity of protein components of human Ro RNPs
- PMID: 15928345
- PMCID: PMC1370793
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7263905
RNA chaperone activity of protein components of human Ro RNPs
Abstract
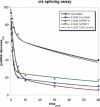
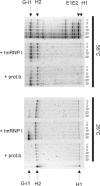
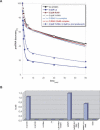
Ro ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes are composed of one molecule of a small noncoding cytoplasmic RNA, termed Y RNA, and the two proteins Ro60 and La. Additional proteins such as hnRNP I, hnRNP K, or nucleolin have recently been shown to be associated with subpopulations of Y RNAs. Ro RNPs appear to be localized in the cytoplasm of all higher eukaryotic cells but their functions have remained elusive. To shed light on possible functions of Ro RNPs, we tested protein components of these complexes for RNA chaperone properties employing two in vitro chaperone assays and additionally an in vivo chaperone assay. In these assays the splicing activity of a group I intron is measured. La showed pronounced RNA chaperone activity in the cis-splicing assay in vitro and also in vivo, whereas no activity was seen in the trans-splicing assay in vitro. Both hnRNP I and hnRNP K exhibited strong chaperone activity in the two in vitro assays, however, proved to be cytotoxic in the in vivo assay. No chaperone activity was observed for Ro60 in vitro and a moderate activity was detected in vivo. In vitro chaperone activities of La and hnRNP I were completely inhibited upon binding of Y RNA. Taken together, these data suggest that the Ro RNP components La, hnRNP K, and hnRNP I possess RNA chaperone activity, while Ro60-Y RNA complexes might function as transporters, bringing other Y RNA binding proteins to their specific targets.
Figures


References
-
- Ali, N., Pruijn, G.J., Kenan, D.J., Keene, J.D., and Siddiqui, A. 2000. Human La antigen is required for the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 27531–27540. - PubMed
-
- Brown, E.C. and Jackson, R.J. 2004. All five cold-shock domains of unr (upstream of N-ras) are required for stimulation of human rhinovirus RNA translation. J. Gen. Virol. 85: 2279–2287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
