HOXB13 is downregulated in colorectal cancer to confer TCF4-mediated transactivation
- PMID: 15928669
- PMCID: PMC2361828
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602631
HOXB13 is downregulated in colorectal cancer to confer TCF4-mediated transactivation
Abstract
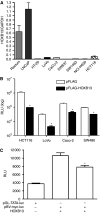
Mutations in the Wnt signalling cascade are believed to cause aberrant proliferation of colorectal cells through T-cell factor-4 (TCF4) and its downstream growth-modulating factors. HOXB13 is exclusively expressed in prostate and colorectum. In prostate cancers, HOXB13 negatively regulates beta-catenin/TCF4-mediated transactivation and subsequently inhibits cell growth. To study the role of HOXB13 in colorectal tumorigenesis, we evaluated the expression of HOXB13 in 53 colorectal tumours originated from the distal left colon to rectum with their matching normal tissues using quantitative RT-PCR analysis. Expression of HOXB13 is either lost or diminished in 26 out of 42 valid tumours (62%), while expression of TCF4 RNA is not correlated with HOXB13 expression. TCF4 promoter analysis showed that HOXB13 does not regulate TCF4 at the transcriptional level. However, HOXB13 downregulated the expression of TCF4 and its target gene, c-myc, at the protein level and consequently inhibited beta-catenin/TCF-mediated signalling. Functionally, forced expression of HOXB13 drove colorectal cancer (CRC) cells into growth suppression. This is the first description of the downregulation of HOXB13 in CRC and its mechanism of action is mediated through the regulation of TCF4 protein stability. Our results suggest that loss of HOXB13 may be an important event for colorectal cell transformation, considering that over 90% of colorectal tumours retain mutations in the APC/beta-catenin pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Involvement of splicing factor-1 in beta-catenin/T-cell factor-4-mediated gene transactivation and pre-mRNA splicing.Gastroenterology. 2007 Mar;132(3):1039-54. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17383426
-
ITF2 prevents activation of the β-catenin-TCF4 complex in colon cancer cells and levels decrease with tumor progression.Gastroenterology. 2014 Aug;147(2):430-442.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.047. Epub 2014 May 15. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24846398
-
Role of a BCL9-related beta-catenin-binding protein, B9L, in tumorigenesis induced by aberrant activation of Wnt signaling.Cancer Res. 2004 Dec 1;64(23):8496-501. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2254. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15574752
-
Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway.Oncogene. 2006 Dec 4;25(57):7531-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210059. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 17143297 Review.
-
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway as a novel cancer drug target.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004 Dec;4(8):653-71. doi: 10.2174/1568009043332709. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 15578921 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of homeobox B-13 correlates with angiogenesis, aberrant expression of EMT markers, aggressive characteristics and poor prognosis in pancreatic carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6919-27. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261579 Free PMC article.
-
HMCan: a method for detecting chromatin modifications in cancer samples using ChIP-seq data.Bioinformatics. 2013 Dec 1;29(23):2979-86. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt524. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 24021381 Free PMC article.
-
Homeobox D10 gene, a candidate tumor suppressor, is downregulated through promoter hypermethylation and associated with gastric carcinogenesis.Mol Med. 2012 May 9;18(1):389-400. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00172. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22160393 Free PMC article.
-
HoxB13 expression in ductal type adenocarcinoma of prostate: clinicopathologic characteristics and its utility as potential diagnostic marker.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):20205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56657-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882852 Free PMC article.
-
The Hox genes and their roles in oncogenesis.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 May;10(5):361-71. doi: 10.1038/nrc2826. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20357775 Review.
References
-
- Amir AL, Barua M, McKnight NC, Cheng S, Yuan X, Balk SP (2003) A direct beta-catenin-independent interaction between androgen receptor and T cell factor 4. J Biol Chem 278: 30828–30834 - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Clevers H (2000) Catenins, Wnt signaling and cancer. Bioessays 22: 961–965 - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Clevers H (2000) Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 103: 311–320 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

