Anti-gastric cancer active immunity induced by FasL/B7-1 gene-modified tumor cells
- PMID: 15929168
- PMCID: PMC4316049
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3204
Anti-gastric cancer active immunity induced by FasL/B7-1 gene-modified tumor cells
Abstract
Aim: To study the activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) against gastric cancer cells induced by FasL/B7-1 (FB-11) gene-modified tumor cells, and to explore whether co-expression of FasL and B7-1 in SGC-7901 tumor cells could initiate synergistic antitumor effect.
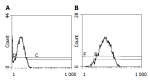
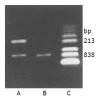
Methods: FasL and B7-1 genes were transfected into human SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells with adenovirus vectors. The positive clones were selected by G418. FasL and B7-1 genes were detected by flow cytometry and RT-PCR. Abdominal infiltrating lymphocytes and sensitized spleen cells were obtained from mice that were immunized with SGC-7901/FB-11 or wild type SGC-7901 cells intraperitoneally, and cytotoxicity of these CTLs against tumor cells was determined by MTT assay.
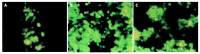
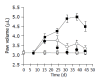
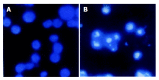
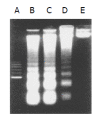
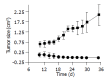
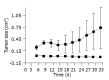
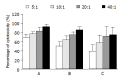
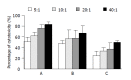
Results: Flow cytometry and RT-PCR showed that FasL and B7-1 genes were highly expressed. FasL and B7-1 transfected cancer cells had a high apoptosis index. DNA laddering suggested that FasL and B7-1 genes induced gastric cancer cell apoptosis. FasL(+)/B7-1(+)SGC-7901 cells (SGC-7901/FB-11) were inoculated subcutaneously in the dorsal skin of C57BL/6 mice and then decreased their tumorigenicity greatly (z = 2.15-46.10, P<0.01). SGC-7901/FB-11 cell-sensitized mice obtained protective immune activity against the rechallenge of wild type SGC-7901 cells (z = 2.06-44.30, P<0.05). The cytotoxicity of CTLs induced by SGC-7901/FB-11 cells against SGC-7901 was significantly higher than that of CTLs activated by wild-type SGC-7901 cells (84.1+/-2.4% vs 30.5+/-2.3%, P<0.05).
Conclusion: FasL and B7-1 genes can effectively promote the activity of CTLs against gastric cancer cells. FasL/B7-1 molecules play an important role in CTL cytotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenovirus-mediated FasL gene transfer into human gastric carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jun 14;11(22):3446-50. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3446. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15948252 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic anti-tumor response induced with epitope-pulsed fibroblasts genetically engineered for B7.1 expression and IFN-gamma secretion.Int J Cancer. 2000 Aug 1;87(3):427-33. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20000801)87:3<427::aid-ijc18>3.0.co;2-j. Int J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10897050
-
Expression of B7 costimulation molecules by colorectal cancer cells reducestumorigenicity and induces anti-tumor immunity.World J Gastroenterol. 1999 Apr;5(2):147-151. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i2.147. World J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 11819415 Free PMC article.
-
From the study of tumor cell immunogenicity to the generation of antitumor cytotoxic cells in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Jul;38(3-4):247-63. doi: 10.3109/10428190009087016. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10830732 Review.
-
On the role and significance of Fas (Apo-1/CD95) ligand (FasL) expression in immune privileged tissues and cancer cells using multiple myeloma as a model.Leuk Lymphoma. 1998 Nov;31(5-6):477-90. doi: 10.3109/10428199809057607. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998. PMID: 9922038 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-2 signals through Sgk1 and inhibits proliferation and apoptosis in kidney cancer cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Jul;85(7):707-21. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0205-2. Epub 2007 Jun 15. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17571248
-
Comprehensive understanding of B7 family in gastric cancer: expression profile, association with clinicopathological parameters and downstream targets.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;16(4):568-582. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.39769. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32025206 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic virus: A catalyst for the treatment of gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1017692. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1017692. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grosenbach DW, Schlom J, Gritz L, Gómez Yafal A, Hodge JW. A recombinant vector expressing transgenes for four T-cell costimulatory molecules (OX40L, B7-1, ICAM-1, LFA-3) induces sustained CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell activation, protection from apoptosis, and enhanced cytokine production. Cell Immunol. 2003;222:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Khatlani TS, Ma Z, Okuda M, Onishi T. Molecular cloning and sequencing of canine T-cell costimulatory molecule (CD28) Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001;78:341–348. - PubMed
-
- Shankar P, Schlom J, Hodge JW. Enhanced activation of rhesus T cells by vectors encoding a triad of costimulatory molecules (B7-1, ICAM-1, LFA-3) Vaccine. 2001;20:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Denfeld RW, Dietrich A, Wuttig C, Tanczos E, Weiss JM, Vanscheidt W, Schöpf E, Simon JC. In situ expression of B7 and CD28 receptor families in human malignant melanoma: relevance for T-cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 1995;62:259–265. - PubMed
-
- Nagai A, Nakagawa E, Hatori K, Choi HB, McLarnon JG, Lee MA, Kim SU. Generation and characterization of immortalized human microglial cell lines: expression of cytokines and chemokines. Neurobiol Dis. 2001;8:1057–1068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

