Expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor subunits alpha1, beta1, gamma2 mRNA in rats with hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 15929193
- PMCID: PMC4316074
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i21.3319
Expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor subunits alpha1, beta1, gamma2 mRNA in rats with hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the mRNA expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABA(A)) receptor subunits alpha(1), beta(1), gamma(2) in different parts of the brain of rats with hepatic encephalopathy.
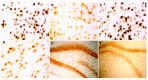
Methods: Twelve adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into two groups: (1) hepatic encephalopathy model group (n = 6), which was induced by intraperitoneal injection of thioacetamide (TAA, 350 mg/kg) for three consecutive days; (2) control group (n = 6), in which the rats were treated with same dose of normal saline solution. After the freeze slice of cerebrum was made, in situ hybridization was used to detect the mRNA of GABAA receptor subunits alpha(1), beta(1), and gamma(2) in rat cerebral cortex, basal nuclei, substantia nigra and hippocampi. Image data were collected and analyzed quantitatively by QWin550CW model image signal gather and analysis system.
Results: In rats with hepatic encephalopathy, mRNA expression levels of GABA(A) receptor subunits alpha(1), beta(1) increased significantly in basal nuclei, substantia nigra pars compacta, substantia nigra pars reticularis and hippocampi (144.7+/-15.67/184.14+/-4.41, 60.61+/-33.66/113.07+/-32.44, 87.71+/- 21.25/128.40+/-18.85, 122.34+/-5.56/161.60+/-4.56, 123.29+/-5.21/140.65+/-4.15, 123.40+/-4.42/140.09+/-4.52, 124.76+/-4.18/140.09+/-4.12, 141.62+/-15.09/182.80 +/-5.20, 69.13+/-30.74/134.21+/-43.76, 87.87+/-25.16/151.01+/-19.49, 122.14+/-6.30 /162.33+/-3.92, 122.81+/-5.09/137.19+/-7.12, 123.00+/-4.63/138.11+/-5.92, 125.75 +/-2.43/138.81+/-6.10, P<0.01), but did not change in the cerebral cortex compared to the control group. Similar changes were found in the mRNA expression levels of GABA(A) receptor subunit gamma(2), which increased significantly in basal nuclei, substantia nigra pars compacta, substantia nigra pars reticularis (136.81+/-26.41/167.97+/-16.23, 51.00+/-36.14/113.18+/-36.52, 86.35+/-20.30/ 126.90+/-19.74, P<0.01), CA1 of hippocampal (162.15+/-9.05/178.62+/-6.45, P<0.05), and no changes were found in the cerebral cortex and CA2, CA3, CA4 of hippocampi.
Conclusion: In rats with hepatic encephalopathy, mRNA expression levels of GABA(A) receptor subunits alpha(1), beta(1), gamma(2) increase significantly in basal nuclei, substantia nigra and hippocampi, suggesting that the changes of mRNA expression levels in GABA(A) receptor subunits may contribute to the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Chu CJ, Lee FY, Wang SS, Chang FY, Lin HC, Wu SL, Chan CC, Tsai YT, Lee SD. Establishment of an animal model of hepatic encephalopathy. Zhonghua YiXue ZaZhi (Taipei) 2000;63:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Jones EA. Ammonia, the GABA neurotransmitter system, and hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2002;17:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Schafer DF, Jones EA. Hepatic encephalopathy and the gamma-aminobutyric-acid neurotransmitter system. Lancet. 1982;1:18–20. - PubMed
-
- Schafer DF, Jones EA. Potential neural mechanisms in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:615–627. - PubMed
-
- Jones EA. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:467–485. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

