MLN64 is involved in actin-mediated dynamics of late endocytic organelles
- PMID: 15930133
- PMCID: PMC1182323
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1105
MLN64 is involved in actin-mediated dynamics of late endocytic organelles
Abstract
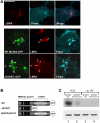
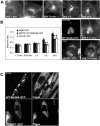
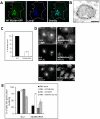
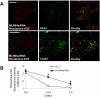
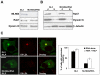
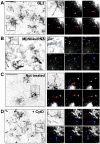
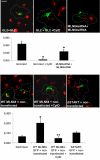
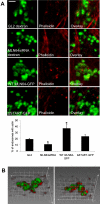
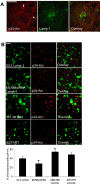
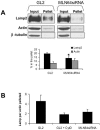
MLN64 is a late endosomal cholesterol-binding membrane protein of an unknown function. Here, we show that MLN64 depletion results in the dispersion of late endocytic organelles to the cell periphery similarly as upon pharmacological actin disruption. The dispersed organelles in MLN64 knockdown cells exhibited decreased association with actin and the Arp2/3 complex subunit p34-Arc. MLN64 depletion was accompanied by impaired fusion of late endocytic organelles and delayed cargo degradation. MLN64 overexpression increased the number of actin and p34-Arc-positive patches on late endosomes, enhanced the fusion of late endocytic organelles in an actin-dependent manner, and stimulated the deposition of sterol in late endosomes harboring the protein. Overexpression of wild-type MLN64 was capable of rescuing the endosome dispersion in MLN64-depleted cells, whereas mutants of MLN64 defective in cholesterol binding were not, suggesting a functional connection between MLN64-mediated sterol transfer and actin-dependent late endosome dynamics. We propose that local sterol enrichment by MLN64 in the late endosomal membranes facilitates their association with actin, thereby governing actin-dependent fusion and degradative activity of late endocytic organelles.
Figures
References
-
- Alpy, F., Stoeckel, M. E., Dierich, A., Escola, J. M., Wendling, C., Chenard, M. P., Vanier, M. T., Gruenberg, J., Tomasetto, C., and Rio, M. C. (2001). The steroidogenic acute regulatory protein homolog MLN64, a late endosomal cholesterol-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4261-4269. - PubMed
-
- Alpy, F., Latchumanan, V. K., Kedinger, V., Janoshazi, A., Thiele, C., Wendling, C., Rio, M. C., and Tomasetto, C. (2005). Functional characterization of the MENTAL domain. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 17945-17952. - PubMed
-
- Alpy, F., Wendling, C., Rio, M. C., and Tomasetto, C. (2002). MENTHO, a MLN64 homologue devoid of the START domain. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 50780-50787. - PubMed
-
- Arai, R., Geffard, M., and Calas, A. (1992). Intensification of labelings of the immunogold silver staining method by gold toning. Brain Res. Bull. 28, 343-345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

