Pontine stimulation overcomes developmental limitations in the neural mechanisms of eyeblink conditioning
- PMID: 15930504
- PMCID: PMC1142453
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.91105
Pontine stimulation overcomes developmental limitations in the neural mechanisms of eyeblink conditioning
Abstract
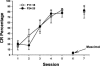
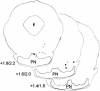
Pontine neuronal activation during auditory stimuli increases ontogenetically between postnatal days (P) P17 and P24 in rats. Pontine neurons are an essential component of the conditioned stimulus (CS) pathway for eyeblink conditioning, providing mossy fiber input to the cerebellum. Here we examined whether the developmental limitation in pontine responsiveness to a CS in P17 rats could be overcome by direct stimulation of the CS pathway. Eyeblink conditioning was established in infant rats on P17-P18 and P24-P25 using pontine stimulation as a CS. There were no significant age-related differences in the rate or level of conditioning. Eyeblink conditioned responses established with the stimulation CS were abolished by inactivation of the ipsilateral cerebellar nuclei and overlying cortex in both age groups. The findings suggest that developmental changes in the CS pathway play an important role in the ontogeny of eyeblink conditioning.
Figures
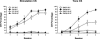

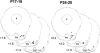
Similar articles
-
Developmental changes in eyeblink conditioning and neuronal activity in the pontine nuclei.Learn Mem. 2003 Sep-Oct;10(5):337-45. doi: 10.1101/lm.63703. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 14557606 Free PMC article.
-
Eyeblink conditioning in rats using pontine stimulation as a conditioned stimulus.Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2004 Jul-Sep;39(3):180-91. doi: 10.1007/BF02734438. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2004. PMID: 15929500 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenetic change in the auditory conditioned stimulus pathway for eyeblink conditioning.Learn Mem. 2008 Oct 30;15(11):823-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.1131208. Print 2008 Nov. Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 18984563 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogenetic changes in the neural mechanisms of eyeblink conditioning.Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2001 Jan-Mar;36(1):15-35. doi: 10.1007/BF02733945. Integr Physiol Behav Sci. 2001. PMID: 11484994 Review.
-
The ontogeny of associative cerebellar learning.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;117:53-72. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420247-4.00004-X. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25172629 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDA receptor involvement in spatial delayed alternation in developing rats.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Feb;123(1):44-53. doi: 10.1037/a0013633. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19170429 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny of septohippocampal modulation of delay eyeblink conditioning.Dev Psychobiol. 2015 Mar;57(2):168-76. doi: 10.1002/dev.21272. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Dev Psychobiol. 2015. PMID: 25604349 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal binge alcohol exposure produces dose dependent deficits in interstimulus interval discrimination eyeblink conditioning in juvenile rats.Brain Res. 2009 Jan 12;1248:162-75. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.040. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19007754 Free PMC article.
-
Ontogeny of trace eyeblink conditioning to shock-shock pairings in the rat pup.Behav Neurosci. 2013 Feb;127(1):114-20. doi: 10.1037/a0031298. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23244289 Free PMC article.
-
Ventral lateral geniculate input to the medial pons is necessary for visual eyeblink conditioning in rats.Learn Mem. 2010 Feb 13;17(2):80-5. doi: 10.1101/lm.1572710. Print 2010 Feb. Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 20154353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizenman, C.D. and Linden, D.J. 2000. Rapid, synaptically driven increases in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar deep nuclear neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 109-111. - PubMed
-
- Bao, S., Chen, L., and Thompson, R.F. 2000. Learning- and cerebellum-dependent neuronal activity in the lateral pontine nucleus. Behav. Neurosci. 114: 254-261. - PubMed
-
- Blatchley, B.J., Cooper, W.A., and Coleman, J.R. 1987. Development of auditory brainstem response to tone pip in the rat. Dev. Brain Res. 32: 75-84. - PubMed
-
- Cartford, M.C., Gohl, E.B., Singson, M., and Lavond, D.G. 1997. The effects of reversible inactivation of the red nucleus on learning-related and auditory-evoked unit activity in the pontine nuclei of classically conditioned rabbits. Learn. Mem. 3: 519-531. - PubMed
-
- Christian, K.M. and Thompson, R.F. 2003. Neural substrates of eyeblink conditioning: Acquisition and retention. Learn. Mem. 10: 427-455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
