AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and dopamine D1 receptor function in the nucleus accumbens core: a context-limited role in the encoding and consolidation of instrumental memory
- PMID: 15930507
- PMCID: PMC1142457
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.93105
AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and dopamine D1 receptor function in the nucleus accumbens core: a context-limited role in the encoding and consolidation of instrumental memory
Abstract
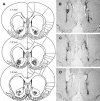
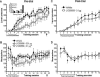
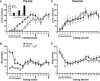
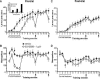
Neural integration of glutamate- and dopamine-coded signals within the nucleus accumbens (NAc) is a fundamental process governing cellular plasticity underlying reward-related learning. Intra-NAc core blockade of NMDA or D1 receptors in rats impairs instrumental learning (lever-pressing for sugar pellets), but it is not known during which phase of learning (acquisition or consolidation) these receptors are recruited, nor is it known what role AMPA/kainate receptors have in these processes. Here we show that pre-trial intra-NAc core administration of the NMDA, AMPA/KA, and D1 receptor antagonists AP-5 (1 microg/0.5 microL), LY293558 (0.01 or 0.1 microg/0.5 microL), and SCH23390 (1 microg/0.5 microL), respectively, impaired acquisition of a lever-pressing response, whereas post-trial administration left memory consolidation unaffected. An analysis of the microstructure of behavior while rats were under the influence of these drugs revealed that glutamatergic and dopaminergic signals contribute differentially to critical aspects of the initial, randomly emitted behaviors that enable reinforcement learning. Thus, glutamate and dopamine receptors are activated in a time-limited fashion-only being required while the animals are actively engaged in the learning context.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Roles of hippocampal NMDA receptors and nucleus accumbens D1 receptors in the amphetamine-produced conditioned place preference in rats.Brain Res Bull. 2008 Dec 16;77(6):412-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.09.007. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Brain Res Bull. 2008. PMID: 18929625
-
Differential involvement of NMDA, AMPA/kainate, and dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in the acquisition and performance of pavlovian approach behavior.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 1;21(23):9471-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09471.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11717381 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of NMDA and AMPA/KA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in instrumental learning guided by reward-predictive cues.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Mar;21(6):1689-702. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03983.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15845096
-
Glutamate-mediated plasticity in corticostriatal networks: role in adaptive motor learning.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Nov;1003:159-68. doi: 10.1196/annals.1300.061. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 14684443 Review.
-
Do AMPA/kainate antagonists possess potential in the treatment of addiction? Evidence from animal behavioural studies.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 2;138:111355. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2025.111355. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40187601 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic shifts in corticostriatal expression patterns of the immediate early genes Homer 1a and Zif268 during early and late phases of instrumental training.Learn Mem. 2006 Sep-Oct;13(5):599-608. doi: 10.1101/lm.335006. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 17015857 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Mechanisms Underlie Long-Term Potentiation at Hippocampus→Medium Spiny Neuron Synapses in the Medial Shell of the Nucleus Accumbens.J Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;44(27):e0100242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0100-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38806250 Free PMC article.
-
The structural basis for mapping behavior onto the ventral striatum and its subdivisions.Brain Struct Funct. 2008 Sep;213(1-2):17-27. doi: 10.1007/s00429-008-0175-3. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Brain Struct Funct. 2008. PMID: 18256852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic administration of morphine is associated with a decrease in surface AMPA GluR1 receptor subunit in dopamine D1 receptor expressing neurons in the shell and non-D1 receptor expressing neurons in the core of the rat nucleus accumbens.Exp Neurol. 2008 Apr;210(2):750-61. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.01.012. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18294632 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles for striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons in dorsolateral striatum in consolidating new instrumental actions.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 25;12(1):5121. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25460-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34433818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, G.E., DeLong, M.R., and Strick, P.L. 1986. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 9: 357-381. - PubMed
-
- Bakshi, V.P. and Kelley, A.E. 1991. Dopaminergic regulation of feeding behavior: Differential effects of haloperidol infusion into three striatal subregions. Psychobiology 19: 223-232.
-
- Baldo, B.A., Sadeghian, K., Basso, A.M., and Kelley, A.E. 2002. Effects of selective dopamine D1 or D2 receptor blockade within nucleus accumbens subregions on ingestive behavior and associated motor activity. Behav. Brain Res. 137: 165-177. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, A.E., Sadeghian, K., Holahan, M.R., and Kelley, A.E. 2002a. Appetitive instrumental learning is impaired by inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase within the nucleus accumbens. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 77: 44-62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
