An entropy-based statistic for genomewide association studies
- PMID: 15931594
- PMCID: PMC1226192
- DOI: 10.1086/431243
An entropy-based statistic for genomewide association studies
Abstract
Efficient genotyping methods and the availability of a large collection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms provide valuable tools for genetic studies of human disease. The standard chi2 statistic for case-control studies, which uses a linear function of allele frequencies, has limited power when the number of marker loci is large. We introduce a novel test statistic for genetic association studies that uses Shannon entropy and a nonlinear function of allele frequencies to amplify the differences in allele and haplotype frequencies to maintain statistical power with large numbers of marker loci. We investigate the relationship between the entropy-based test statistic and the standard chi2 statistic and show that, in most cases, the power of the entropy-based statistic is greater than that of the standard chi2 statistic. The distribution of the entropy-based statistic and the type I error rates are validated using simulation studies. Finally, we apply the new entropy-based test statistic to two real data sets, one for the COMT gene and schizophrenia and one for the MMP-2 gene and esophageal carcinoma, to evaluate the performance of the new method for genetic association studies. The results show that the entropy-based statistic obtained smaller P values than did the standard chi2 statistic.
Figures
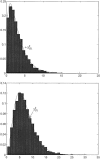
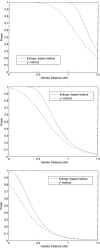
Comment in
-
Estimated haplotype counts from case-control samples cannot be treated as observed counts.Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Apr;78(4):729-30; author reply 728-9. doi: 10.1086/502666. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16532404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
An entropy-based genome-wide transmission/disequilibrium test.Hum Genet. 2007 May;121(3-4):357-67. doi: 10.1007/s00439-007-0322-6. Epub 2007 Feb 13. Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17297624
-
Nonlinear tests for genomewide association studies.Genetics. 2006 Nov;174(3):1529-38. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.060491. Epub 2006 Jul 2. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16816420 Free PMC article.
-
An entropy-based measure for QTL mapping using extreme samples of population.Hum Hered. 2008;65(3):121-8. doi: 10.1159/000109729. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Hum Hered. 2008. PMID: 17934315
-
On selecting markers for association studies: patterns of linkage disequilibrium between two and three diallelic loci.Genet Epidemiol. 2003 Jan;24(1):57-67. doi: 10.1002/gepi.10217. Genet Epidemiol. 2003. PMID: 12508256 Review.
-
Sibship T2 association tests of complex diseases for tightly linked markers.Hum Genomics. 2005 Jun;2(2):90-112. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-2-2-90. Hum Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16004725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Entropy based genetic association tests and gene-gene interaction tests.Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2011 Aug 22;10(1):38. doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1719. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 23089811 Free PMC article.
-
AMBIENCE: a novel approach and efficient algorithm for identifying informative genetic and environmental associations with complex phenotypes.Genetics. 2008 Oct;180(2):1191-210. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.088542. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18780753 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association studies: an information content perspective.Curr Genomics. 2012 Nov;13(7):566-73. doi: 10.2174/138920212803251382. Curr Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23633916 Free PMC article.
-
Comments on the entropy-based transmission/disequilibrium test.Hum Genet. 2008 Feb;123(1):97-100. doi: 10.1007/s00439-007-0450-z. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18060433
-
An adaptive strategy for association analysis of common or rare variants using entropy theory.J Hum Genet. 2017 Aug;62(8):777-781. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.39. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28381878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akey J, Jin L, Xiong M (2001) Haplotypes vs single marker linkage disequilibrium tests: what do we gain? Eur J Hum Genet 9:291–300 - PubMed
-
- Anderson TW (1984) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis. John Wiley & Sons, New York
-
- Bourgain C, Genin E, Margaritte-Jeannin P, Clerget-Darpoux F (2001) Maximum identity length contrast: a powerful method for susceptibility gene detection in isolated populations. Genet Epidemiol Suppl 21:S560–S564 - PubMed
-
- Bourgain C, Genin E, Ober C, Clerget-Darpoux F (2002) Missing data in haplotype analysis: a study on the MILC method. Ann Hum Genet 66:99–108 - PubMed
-
- Bourgain C, Genin E, Quesneville H, Clerget-Darpoux F (2000) Search for multifactorial disease susceptibility genes in founder populations. Ann Hum Genet 64:255–265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

