KCC2 expression in immature rat cortical neurons is sufficient to switch the polarity of GABA responses
- PMID: 15932617
- PMCID: PMC2945502
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04084.x
KCC2 expression in immature rat cortical neurons is sufficient to switch the polarity of GABA responses
Abstract
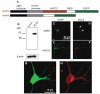
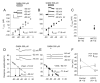
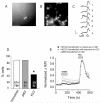
During brain development, GABA and glycine switch from being depolarizing to being hyperpolarizing neurotransmitters. This conversion results from a gradual decrease in the chloride electrochemical equilibrium potential (ECl) of developing neurons, which correlates to an increase in the expression or activity of the potassium chloride cotransporter, KCC2. However, evidence as to whether KCC2 expression is sufficient, in and of itself, to induce this switch is lacking. In order to address this question, we used a gain-of-function approach by over-expressing human KCC2 (hKCC2) in immature cortical neurons, before endogenous up-regulation of KCC2. We found that premature expression of hKCC2 produced a substantial negative shift in the GABA reversal potential and decreased or abolished GABA-elicited calcium responses in cultured neurons. We conclude that KCC2 expression is not only necessary but is also sufficient for ending the depolarizing period of GABA in developing cortical neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
WNK1-regulated inhibitory phosphorylation of the KCC2 cotransporter maintains the depolarizing action of GABA in immature neurons.Sci Signal. 2015 Jun 30;8(383):ra65. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa0354. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26126716
-
Cortical neurons lacking KCC2 expression show impaired regulation of intracellular chloride.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Mar;93(3):1557-68. doi: 10.1152/jn.00616.2004. Epub 2004 Oct 6. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15469961
-
Cation-chloride cotransporters and GABA-ergic innervation in the human epileptic hippocampus.Epilepsia. 2007 Apr;48(4):663-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.00986.x. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Epilepsia. 2007. PMID: 17319917
-
Sexually dimorphic expression of KCC2 and GABA function.Epilepsy Res. 2008 Aug;80(2-3):99-113. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2008.04.013. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Epilepsy Res. 2008. PMID: 18524541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two developmental switches in GABAergic signalling: the K+-Cl- cotransporter KCC2 and carbonic anhydrase CAVII.J Physiol. 2005 Jan 1;562(Pt 1):27-36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.077495. Epub 2004 Nov 4. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15528236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the neuronal K-Cl co-transporter KCC2 in inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission.Front Cell Neurosci. 2012 Feb 21;6:5. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2012.00005. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22363264 Free PMC article.
-
The cation-chloride cotransporter NKCC1 promotes sharp waves in the neonatal rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2006 Jun 15;573(Pt 3):765-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.107086. Epub 2006 Apr 27. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16644806 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Expression of KCC2 in the α Cells of Normal and Type 1 Diabetes Model Mouse Pancreatic Islets.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Feb 26;55(1):47-56. doi: 10.1267/ahc.21-00078. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 35444351 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular zinc inhibits KCC2 transporter activity.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Jun;12(6):725-7. doi: 10.1038/nn.2316. Epub 2009 May 10. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19430470 Free PMC article.
-
SNARE-dependent upregulation of potassium chloride co-transporter 2 activity after metabotropic zinc receptor activation in rat cortical neurons in vitro.Neuroscience. 2012 May 17;210:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22441041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben Ari Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: the nature of the nurture. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Ben Ari Y, Khazipov R, Leinekugel X, Caillard O, Gaiarsa JL. GABAA, NMDA and AMPA receptors: a developmentally regulated ‘menage a trois’. TINS. 1997;20:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Breitwieser GE, Altamirano AA, Russell JM. Osmotic stimulation of Na(+)-K(+)-Cl− cotransport in squid giant axon is [Cl−]i dependent. Am. J. Physiol. 1990;258:C749–C753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

