Involvement of bacterial quorum-sensing signals in spoilage of bean sprouts
- PMID: 15933035
- PMCID: PMC1151799
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3321-3330.2005
Involvement of bacterial quorum-sensing signals in spoilage of bean sprouts
Abstract
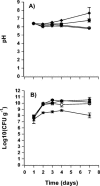
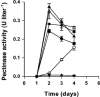
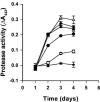
Bacterial communication signals, acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs), were extracted from samples of commercial bean sprouts undergoing soft-rot spoilage. Bean sprouts produced in the laboratory did not undergo soft-rot spoilage and did not contain AHLs or AHL-producing bacteria, although the bacterial population reached levels similar to those in the commercial sprouts, 10(8) to 10(9) CFU/g. AHL-producing bacteria (Enterobacteriaceae and pseudomonads) were isolated from commercial sprouts, and strains that were both proteolytic and pectinolytic were capable of causing soft-rot spoilage in bean sprouts. Thin-layer chromatography and liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry revealed the presence of N-3-oxo-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone in spoiled bean sprouts and in extracts from pure cultures of bacteria. During normal spoilage, the pH of the sprouts increased due to proteolytic activity, and the higher pH probably facilitated the activity of pectate lyase. The AHL synthetase gene (I gene) from a spoilage Pectobacterium was cloned, sequenced, and inactivated in the parent strain. The predicted amino acid sequence showed 97% homology to HslI and CarI in Erwinia carotovora. Spoilage of laboratory bean sprouts inoculated with the AHL-negative mutant was delayed compared to sprouts inoculated with the wild type, and the AHL-negative mutant did not cause the pH to rise. Compared to the wild-type strain, the AHL-negative mutant had significantly reduced protease and pectinase activities and was negative in an iron chelation (siderophore) assay. This is the first study demonstrating AHL regulation of iron chelation in Enterobacteriaceae. The present study clearly demonstrates that the bacterial spoilage of some food products is influenced by quorum-sensing-regulated phenotypes, and understanding these processes may be useful in the development of novel food preservation additives that specifically block the quorum-sensing systems.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Presence of acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) and AHL-producing bacteria in meat and potential role of AHL in spoilage of meat.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jul;70(7):4293-302. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.7.4293-4302.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15240313 Free PMC article.
-
Well-known quorum sensing inhibitors do not affect bacterial quorum sensing-regulated bean sprout spoilage.J Appl Microbiol. 2007 Mar;102(3):826-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03121.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17309633
-
Quorum sensing signal molecules (acylated homoserine lactones) in gram-negative fish pathogenic bacteria.Dis Aquat Organ. 2005 Jun 14;65(1):43-52. doi: 10.3354/dao065043. Dis Aquat Organ. 2005. PMID: 16042042
-
N-acyl homoserinelactone-mediated gene regulation in gram-negative bacteria.Syst Appl Microbiol. 1999 Dec;22(4):493-506. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(99)80001-0. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10794136 Review.
-
Quorum sensing in Serratia.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007 Jul;31(4):407-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00071.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17459113 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonbioluminescent strains of Photobacterium phosphoreum produce the cell-to-cell communication signal N-(3-Hydroxyoctanoyl)homoserine lactone.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Apr;71(4):2113-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.4.2113-2120.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15812045 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a solo acylhomoserine lactone synthase from the myxobacterium Archangium gephyra.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 4;11(1):3018. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82480-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33542315 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) in beef by spice marination.J Food Sci Technol. 2016 Jun;53(6):2686-94. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2240-x. Epub 2016 May 30. J Food Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27478224 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato Plant Microbiota under Conventional and Organic Fertilization Regimes in a Soilless Culture System.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 22;11(7):1633. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071633. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512805 Free PMC article.
-
Oregano essential oil-pectin edible films as anti-quorum sensing and food antimicrobial agents.Front Microbiol. 2014 Dec 17;5:699. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00699. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25566215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexeyev, M. F., and I. N. Shokolenko. 1995. Mini-Tn10 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis and gene delivery into the chromosome of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 160:59-62. - PubMed
-
- Andersson, R. A., A. R. Eriksson, R. Heikinheimo, A. Mae, M. Pirhonen, V. Koiv, H. Hyytianen, A. Tuikkala, and E. T. Palva. 2000. Quorum sensing in the plant pathogen Erwinia caratovora subsp. carotovora: the role of expREcc. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 13:384-393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

