Genomic DNA amplification from a single bacterium
- PMID: 15933038
- PMCID: PMC1151817
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3342-3347.2005
Genomic DNA amplification from a single bacterium
Abstract
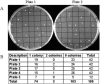
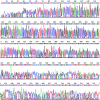
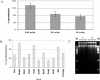
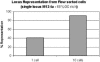
Genomic DNA was amplified about 5 billion-fold from single, flow-sorted bacterial cells by the multiple displacement amplification (MDA) reaction, using phi 29 DNA polymerase. A 662-bp segment of the 16S rRNA gene could be accurately sequenced from the amplified DNA. MDA methods enable new strategies for studying non-culturable microorganisms.
Figures
References
-
- Dean, F. B., S. Hosono, L. Fang, X. Wu, A. F. Faruqi, P. Bray-Ward, Z. Sun, Q. Zong, Y. Du, J. Du, M. Driscoll, W. Song, S. F. Kingsmore, M. Egholm, and R. S. Lasken. 2002. Comprehensive human genome amplification using multiple displacement amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:5261-5266. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Detter, J. C., J. M. Jett, S. M. Lucas, E. Dalin, A. R. Arellano, M. Wang, J. R. Nelson, J. Chapman, Y. Lou, D. Rokhsar, T. L. Hawkins, and P. M. Richardson. 2002. Isothermal strand-displacement amplification applications for high-throughput genomics. Genomics 80:691-698. - PubMed
-
- Handyside, A. H., M. D. Robinson, R. J. Simpson, M. Omar, Marie-Anne Shaw, J. G. Grudzinskas, and A. Rutherford. 2004. Isothermal whole genome amplification from single and small numbers of cells: a new era for preimplantation genetic diagnosis of inherited disease. Mol. Hum. Reprod. Epub 20 August 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

