The Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase is coupled to and antagonized by the Ubp2 deubiquitinating enzyme
- PMID: 15933713
- PMCID: PMC1173151
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600710
The Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase is coupled to and antagonized by the Ubp2 deubiquitinating enzyme
Abstract
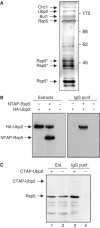
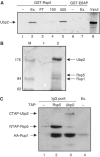
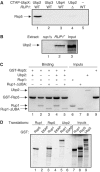
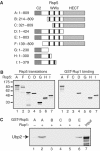
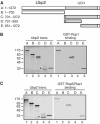
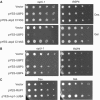
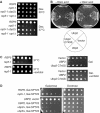
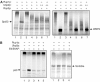
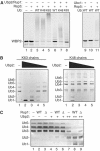
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rsp5 is an essential HECT ubiquitin ligase involved in several biological processes. To gain further insight into regulation of this enzyme, we identified proteins that copurified with epitope-tagged Rsp5. Ubp2, a deubiquitinating enzyme, was a prominent copurifying protein. Rup1, a previously uncharacterized UBA domain protein, was required for binding of Rsp5 to Ubp2 both in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression of Ubp2 or Rup1 in the rsp5-1 mutant elicited a strong growth defect, while overexpression of a catalytically inactive Ubp2 mutant or Rup1 deleted of the UBA domain did not, suggesting an antagonistic relationship between Rsp5 and the Ubp2/Rup1 complex. Consistent with this model, rsp5-1 temperature sensitivity was suppressed by either ubp2Delta or rup1Delta mutations. Ubp2 reversed Rsp5-catalyzed substrate ubiquitination in vitro, and Rsp5 and Ubp2 preferentially assembled and disassembled, respectively, K63-linked polyubiquitin chains. Together, these results indicate that Rsp5 activity is modulated by being physically coupled to the Rup1/Ubp2 deubiquitinating enzyme complex, representing a novel mode of regulation for an HECT ubiquitin ligase.
Figures
References
-
- Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M (2004) Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1695: 189–207 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R (2003) Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 424: 797–801 - PubMed
-
- Canning M, Boutell C, Parkinson J, Everett RD (2004) A RING finger ubiquitin ligase is protected from autocatalyzed ubiquitination and degradation by binding to ubiquitin-specific protease USP7. J Biol Chem 279: 38160–38168 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

