Damage and threshold shift resulting from cochlear exposure to paraquat-generated superoxide
- PMID: 15935579
- PMCID: PMC1987394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2005.03.025
Damage and threshold shift resulting from cochlear exposure to paraquat-generated superoxide
Abstract
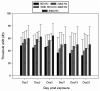
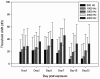
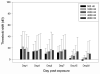
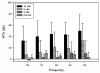
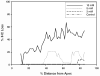
Superoxide has been implicated as a contributing factor to cochlear pathology from a number of sources, including noise and ototoxic drugs. The effects of NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide on the cochlea were investigated in the current study using paraquat (PQ). PQ is a toxic herbicide that causes tissue damage by generating superoxide through reduction of molecular oxygen in a reaction catalyzed by NADPH oxidase. The current study examined the effects of round window PQ administration on inferior colliculus (IC) evoked potential thresholds (EVP) and hair cell damage. Using implanted IC electrodes, chinchillas were tested for IC EVP thresholds before and after PQ exposure. Ears were exposed to PQ at one of four concentrations: 10, 5, 3 mM, and vehicle control. Thresholds were increased in a dose-dependent manner, and peaked between one and seven days post-exposure. Thresholds then showed a small amount of recovery before reaching PTS by Day 22. Outer and inner hair cell losses were consistent with PTS. The similarities between PQ ototoxicity and noise-induced hearing loss suggest the possibility of similar biochemical pathways involving superoxide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
siRNA-mediated knock-down of NOX3: therapy for hearing loss?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(14):2429-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3. Epub 2012 May 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Bak and Sirt3 in Paraquat-Induced Cochlear Hair Cell Damage.Neurotox Res. 2021 Aug;39(4):1227-1237. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00366-6. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 33900547 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant treatment reduces blast-induced cochlear damage and hearing loss.Hear Res. 2012 Mar;285(1-2):29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.01.013. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22326291
-
R-phenylisopropyladenosine attenuates noise-induced hearing loss in the chinchilla.Hear Res. 1997 Nov;113(1-2):198-206. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(97)00143-3. Hear Res. 1997. PMID: 9387999
-
Hidden Hearing Loss: A Disorder with Multiple Etiologies and Mechanisms.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Jan 2;10(1):a035493. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035493. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020. PMID: 30617057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with work accidents in a rural area in Minas Gerais, Brazil.Rev Bras Med Trab. 2020 Apr 15;17(3):378-386. doi: 10.5327/Z1679443520190318. eCollection 2019. Rev Bras Med Trab. 2020. PMID: 32368672 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-mediated knock-down of NOX3: therapy for hearing loss?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(14):2429-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3. Epub 2012 May 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH Oxidase 3: Beyond the Inner Ear.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;13(2):219. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020219. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of deliberate ingestion of organophosphate or paraquat on brain stem auditory-evoked potentials.J Med Toxicol. 2011 Dec;7(4):277-80. doi: 10.1007/s13181-011-0173-3. J Med Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21833797 Free PMC article.
-
NOX3 NADPH oxidase couples transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 to signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-mediated inflammation and hearing loss.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Mar 15;14(6):999-1010. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3497. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 20712533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böheim K, Bichler E. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Audiometric findings and experimental cochlear pathology. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1985;242:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KC, Rybak LP, Meech RP, Hughes L. d-methionine provides excellent protection from cisplatin ototoxicity in the rat. Hear. Res. 1996;102:90–98. - PubMed
-
- Clerici WJ, Yang L. Direct effects of intraperilymphatic reactive oxygen species generation on cochlear function. Hear. Res. 1996;101:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Clerici WJ, Hensley K, DiMartino DL, Butterfield DA. Direct detection of ototoxicant-induced reactive oxygen species generation in cochlear explants. Hear. Res. 1996;98:116–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

