Reduction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection in swine alveolar macrophages by porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2)-induced interferon-alpha
- PMID: 15936905
- PMCID: PMC7117408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.03.010
Reduction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) infection in swine alveolar macrophages by porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2)-induced interferon-alpha
Abstract
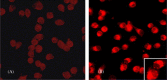
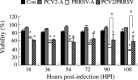
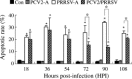
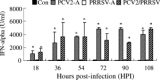
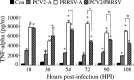
Two common viral pathogens of swine, namely, porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), were investigated in regard to their effects on monolayer cultures of swine alveolar macrophages (AMs). The purpose was to identify selected cellular changes and responses potentially associated with the clinical reactions of pigs infected with either or both of these viruses. Measurements included the (1) absolute and relative numbers of infected, viable, and apoptotic cells; (2) distribution of viral antigens; (3) levels of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) produced and their association with the extent of virus-induced cytopathology. Four groups of AMs were studied, including mock-infected, PCV2 alone-infected (PCV2-A), PRRSV alone-infected (PRRSV-A), and PCV2 and PRRSV dually infected (PCV2/PRRSV) groups. The AMs of PCV2-A group had high antigen-containing rate without cell death. There was a marked increase in cell death and apoptosis in PRRSV-A group. However, a lower PRRSV-induced infectious rate, cell death, and apoptosis were seen in PCV2/PRRSV group. High levels of IFN-alpha production were detected in PCV2-infected groups, but not in mock-infected and PRRSV-A groups. The PRRSV-induced cytopathic effect (CPE) on MARC-145 cells or swine AMs was markedly reduced by pre-incubation of the cells with UV-treated or non-UV-treated supernatants of PCV2-infected AMs. In addition, the reduction in CPE was abolished when the supernatants of PCV2-infected AMs were pre-treated with a mouse anti-recombinant porcine IFN-alpha antibody. The results suggest that swine AMs were an important reservoir of PCV2; PCV2 infection reduced PRRSV infection and PRRSV-associated CPE in PCV2/PRRSV AMs; the reduction of PRRSV infection in AMs was mediated by IFN-alpha generated by PCV2 infection. The reduced PRRSV-associated CPE in AMs and increased pro-inflammatory cytokine production may lead to a more severe pneumonic lesion in those dually infected pigs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of infection order of porcine circovirus type 2 and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on dually infected swine alveolar macrophages.BMC Vet Res. 2012 Sep 25;8:174. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-174. BMC Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 23009687 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of an interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) mutant of porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) on PCV2-induced pathological lesions in a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) co-infection model.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Jan 10;147(1-2):49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.06.010. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20637549
-
Comparative effects of vaccination against porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in a PCV2-PRRSV challenge model.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Mar;20(3):369-76. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00497-12. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23302743 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine respiratory disease complex: Interaction of vaccination and porcine circovirus type 2, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Vet J. 2016 Jun;212:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.10.030. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Vet J. 2016. PMID: 27256017 Review.
-
Antagonizing interferon-mediated immune response by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:315470. doi: 10.1155/2014/315470. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25101271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant host immune response induced by highly virulent PRRSV identified by digital gene expression tag profiling.BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 7;11:544. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-544. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20929578 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) increases the expression of endothelial adhesion/junction molecules.Braz J Microbiol. 2016 Oct-Dec;47(4):870-875. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Braz J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27522934 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar Macrophages in Viral Respiratory Infections: Sentinels and Saboteurs of Lung Defense.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 5;26(1):407. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010407. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39796262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of infection order of porcine circovirus type 2 and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on dually infected swine alveolar macrophages.BMC Vet Res. 2012 Sep 25;8:174. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-174. BMC Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 23009687 Free PMC article.
-
The Swine IFN System in Viral Infections: Major Advances and Translational Prospects.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 27;11(2):175. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020175. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albina E., Carrat C., Charley B. Interferon-alpha response to swine arterivirus (PoAV), the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998;18:485–490. - PubMed
-
- Allan G.M., Ellis J.A. Porcine circoviruses: a review. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2000;12:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Allan G.M., McNeilly F., Ellis J.A., Krakowka S., Meehan B.M., McNair I., Walker I., Kennedy S. Experimental infection of colostrum deprived piglets with porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) potentiates PCV2 replication. Arch. Virol. 2000;145:2421–2429. - PubMed
-
- Allan G.M., McNeilly F., Kennedy S., Daft B., Clark E.G., Ellis J.A., Haines D.M., Meehan B.M., Adair B.M. Isolation of porcine circovirus-like viruses from pigs with a wasting disease in the USA and Europe. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 1998;10:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Ankel H., Westra D.F., Welling-Wester S., Lebon P. Induction of interferon-α by glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus: a possible role of chemokine receptors. Virology. 1998;251:317–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

