Analysis of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 gene expression in the maize rhizosphere: in vivo [corrected] expression technology capture and identification of root-activated promoters
- PMID: 15937166
- PMCID: PMC1151710
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.12.4033-4041.2005
Analysis of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 gene expression in the maize rhizosphere: in vivo [corrected] expression technology capture and identification of root-activated promoters
Erratum in
- J Bacteriol. 2005 Aug;187(15):5504
Abstract
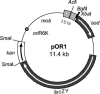
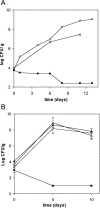
Pseudomonas putida KT2440, a paradigm organism in biodegradation and a good competitive colonizer of the maize rhizosphere, was the subject of studies undertaken to establish the genetic determinants important for its rhizospheric lifestyle. By using in vivo expression technology (IVET) to positively select single cell survival, we identified 28 rap genes (root-activated promoters) preferentially expressed in the maize rhizosphere. The IVET system had two components: a mutant affected in aspartate-beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (asd), which was unable to survive in the rhizosphere, and plasmid pOR1, which carries a promoter-less asd gene. pOR1-borne transcriptional fusions of the rap promoters to the essential gene asd, which were integrated into the chromosome at the original position of the corresponding rap gene, were active and allowed growth of the asd strain in the rhizosphere. The fact that five of the rap genes identified in the course of this work had been formerly characterized as being related to root colonization reinforced the IVET approach. Up to nine rap genes encoded proteins either of unknown function or that had been assigned an unspecific role based on conservation of the protein family domains. Rhizosphere-induced fusions included genes with probable functions in the cell envelope, chemotaxis and motility, transport, secretion, DNA metabolism and defense mechanism, regulation, energy metabolism, stress, detoxification, and protein synthesis.
Figures


References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

