The transcription termination factor Rho is essential and autoregulated in Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 15937192
- PMCID: PMC1151746
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.12.4290-4294.2005
The transcription termination factor Rho is essential and autoregulated in Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
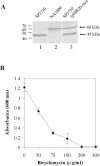
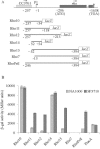
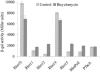
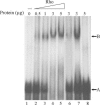
The impossibility of obtaining a rho null mutant and sensitivity to bicyclomycin have indicated that rho is essential for the viability of Caulobacter crescentus. Transcription gene fusions of sequences with serial deletions of the rho 5' untranslated region (5'-UTR) with a lacZ reporter gene indicated that rho is autoregulated at the level of attenuation of transcription in the 5'-UTR.
Figures

References
-
- Alifano, P., F. Rivellini, D. Limauro, C. B. Bruni, and M. S. Carlomagno. 1991. A consensus motif common to all Rho-dependent prokaryotic transcription terminators. Cell 64:553-563. - PubMed
-
- Barik, S., P. Bhattacharya, and A. Das. 1985. Autogenous regulation of transcription termination factor Rho. J. Mol. Biol. 182:495-508. - PubMed
-
- Bektesh, S. L., and J. P. Richardson. 1980. A rho-recognition site on phage lambda cro-gene mRNA. Nature 283:102-104. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, C. A., A. J. Dombroski, and T. Platt. 1987. Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell 48:945-952. - PubMed
-
- Chen, X., and B. L. Stitt. 2004. The binding of C10 oligomers to Escherichia coli transcription termination factor Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 279:16301-16310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

