Global analysis of positive and negative pre-mRNA splicing regulators in Drosophila
- PMID: 15937219
- PMCID: PMC1142554
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1314205
Global analysis of positive and negative pre-mRNA splicing regulators in Drosophila
Abstract
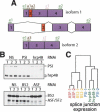
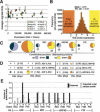
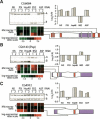
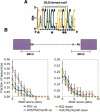
To gain insight into splicing regulation, we developed a microarray to assay all annotated alternative splicing events in Drosophila melanogaster and identified the alternative splice events controlled by four splicing regulators: dASF/SF2, B52/SRp55, hrp48, and PSI. The number of events controlled by each of these factors was found to be highly variable: dASF/SF2 strongly affects >300 splicing events, whereas PSI strongly affects only 43 events. Pairwise analysis also revealed many instances of splice site usage affected by multiple factors and provides the framework to understand the network controlling the alternatively spliced mRNA isoforms that compose the Drosophila transcriptome.
Figures
References
-
- Black D.L. 2003. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72 291-336 - PubMed
-
- Brett D., Pospisil, H., Valcarcel, J., Reich, J., and Bork, P. 2002. Alternative splicing and genome complexity. Nat. Genet. 30 29-30. - PubMed
-
- Burckin T., Nagel, R., Mandel-Gutfreund, Y., Shiue, L., Clark, T.A., Chong, J.L., Chang, T.H., Squazzo, S., Hartzog, G., and Ares Jr., M. 2005. Exploring functional relationships between components of the gene expression machinery. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12 175-182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
