Visualization of diffuse centromeres with centromere-specific histone H3 in the holocentric plant Luzula nivea
- PMID: 15937225
- PMCID: PMC1167539
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.032961
Visualization of diffuse centromeres with centromere-specific histone H3 in the holocentric plant Luzula nivea
Abstract
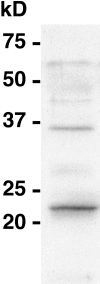
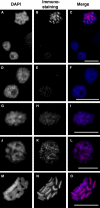
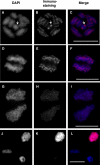
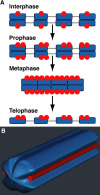
Although holocentric species are scattered throughout the plant and animal kingdoms, only holocentric chromosomes of the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans have been analyzed with centromeric protein markers. In an effort to determine the holocentric structure in plants, we investigated the snowy woodrush Luzula nivea. From the young roots, a cDNA encoding a putative centromere-specific histone H3 (LnCENH3) was successfully isolated based on sequence similarity among plant CENH3s. The deduced amino acid sequence was then used to raise an anti-LnCENH3 antibody. Immunostaining clearly revealed the diffuse centromere-like structure that appears in the linear shape at prophase to telophase. Furthermore, it was shown that the amount of LnCENH3 decreased significantly at interphase. The polar side positioning on each chromatid at metaphase to anaphase also confirmed that LnCENH3 represents one of the centromere-specific proteins in L. nivea. These data from L. nivea are compared with those from C. elegans, and common features of holocentric chromosomes are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of holocentric centromeres of Luzula species.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005;109(1-3):134-43. doi: 10.1159/000082392. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 15753569
-
The holocentric species Luzula elegans shows interplay between centromere and large-scale genome organization.Plant J. 2013 Feb;73(4):555-65. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12054. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 23078243
-
Mitotic microtubule development and histone H3 phosphorylation in the holocentric chromosomes of Rhynchospora tenuis (Cyperaceae).Genetica. 2006 Jan;126(1-2):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s10709-005-1430-7. Genetica. 2006. PMID: 16502083
-
An overview of plant centromeres.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Sep;36(9):529-37. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60144-7. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19782954 Review.
-
Super-Resolution Microscopy Reveals Diversity of Plant Centromere Architecture.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 15;21(10):3488. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103488. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32429054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ultrastructure of mono- and holocentric plant centromeres: an immunological investigation by structured illumination microscopy and scanning electron microscopy.Chromosoma. 2015 Dec;124(4):503-17. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0521-1. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 26048589
-
Holokinetic centromeres and efficient telomere healing enable rapid karyotype evolution.Chromosoma. 2015 Dec;124(4):519-28. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0524-y. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 26062516
-
Extensive conserved synteny of genes between the karyotypes of Manduca sexta and Bombyx mori revealed by BAC-FISH mapping.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 15;4(10):e7465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007465. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19829706 Free PMC article.
-
A simple model explains the cell cycle-dependent assembly of centromeric nucleosomes in holocentric species.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 20;49(16):9053-9065. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab648. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34352103 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of positive selection on CenH3 in Luzula suggests that holokinetic chromosomes may suppress centromere drive.Ann Bot. 2016 Dec;118(7):1347-1352. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw186. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Ann Bot. 2016. PMID: 27616209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amor, D.J., Kalitsis, P., Sumer, H., and Choo, K.H. (2004). Building the centromere: From foundation proteins to 3D organization. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 359–368. - PubMed
-
- Black, B.E., Foltz, D.R., Chakravarthy, S., Luger, K., Woods, V.L., Jr., and Cleveland, D.W. (2004). Structural determinants for generating centromeric chromatin. Nature 430, 578–582. - PubMed
-
- Buchwitz, B.J., Ahmad, K., Moore, L.L., Roth, M.B., and Henikoff, S. (1999). A histone-H3-like protein in C. elegans. Nature 401, 547–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

