Urea-induced denaturation of apolipoprotein serum amyloid A reveals marginal stability of hexamer
- PMID: 15937280
- PMCID: PMC2253367
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.051387005
Urea-induced denaturation of apolipoprotein serum amyloid A reveals marginal stability of hexamer
Abstract
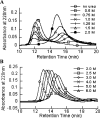
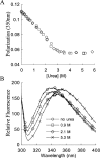
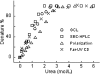
Serum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute phase reactant protein that is predominantly found bound to high-density lipoprotein in plasma. Upon inflammation, the plasma concentration of SAA can increase dramatically, occasionally leading to the development of amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis, which involves the deposition of SAA amyloid fibrils in major organs. We previously found that the murine isoform SAA2.2 exists in aqueous solution as a hexamer containing a central channel. Here we show using various biophysical and biochemical techniques that the SAA2.2 hexamer can be totally dissociated into monomer by approximately 2 M urea, with the concerted loss of its alpha-helical structure. However, limited trypsin proteolysis experiments in urea showed a conserved digestion profile, suggesting the preservation of major backbone topological features in the urea-denatured state of SAA2.2. The marginal stability of hexameric SAA2.2 and the presence of residual structure in the denatured monomeric protein suggest that both forms may interconvert in vivo to exert different functions to meet the various needs during normal physiological conditions and in response to inflammatory stimuli.
Figures



References
-
- Ancsin, J.B. and Kisilevsky, R. 1999a. The heparin/heparan sulfate-binding site on apo-serum amyloid A. Implications for the therapeutic intervention of amyloidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 274 7172–7181. - PubMed
-
- ———. 1999b. Laminin interactions with the apoproteins of acute-phase HDL: Preliminary mapping of the laminin binding site on serum amyloid A. Amyloid 6 37–47. - PubMed
-
- Checovich, W.J., Bolger, R.E., and Burke, T. 1995. Fluorescence polarization —A new tool for cell and molecular biology. Nature 375 254–256. - PubMed
-
- Colón, W. 1999. Analysis of protein structure by solution optical spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 309 605–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

