MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies
- PMID: 15937477
- PMCID: PMC1855297
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1274
MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies
Abstract
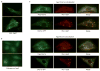
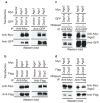
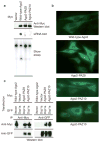
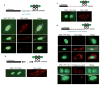
Small RNAs, including small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) can silence target genes through several different effector mechanisms. Whereas siRNA-directed mRNA cleavage is increasingly understood, the mechanisms by which miRNAs repress protein synthesis are obscure. Recent studies have revealed the existence of specific cytoplasmic foci, referred to herein as processing bodies (P-bodies), which contain untranslated mRNAs and can serve as sites of mRNA degradation. Here we demonstrate that Argonaute proteins--the signature components of the RNA interference (RNAi) effector complex, RISC--localize to mammalian P-bodies. Moreover, reporter mRNAs that are targeted for translational repression by endogenous or exogenous miRNAs become concentrated in P-bodies in a miRNA-dependent manner. These results provide a link between miRNA function and mammalian P-bodies and suggest that translation repression by RISC delivers mRNAs to P-bodies, either as a cause or as a consequence of inhibiting protein synthesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
RNAi and the P-body connection.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;7(7):643-4. doi: 10.1038/ncb0705-643. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15990892 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

