A Ser/Thr cluster within the C-terminal domain of the rat prostaglandin receptor EP3alpha is essential for agonist-induced phosphorylation, desensitization and internalization
- PMID: 15937517
- PMCID: PMC1576232
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706282
A Ser/Thr cluster within the C-terminal domain of the rat prostaglandin receptor EP3alpha is essential for agonist-induced phosphorylation, desensitization and internalization
Abstract
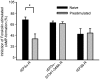
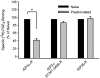
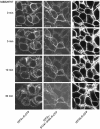
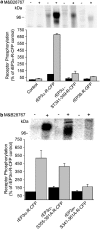
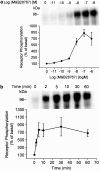
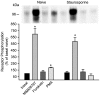
Two isoforms of the rat prostaglandin E(2) receptor, rEP3alpha-R and rEP3beta-R, differ only in their C-terminal domain. To analyze the function of the rEP3-R C-terminal domain in agonist induced desensitization, a cluster of Ser/Thr residues in the C-terminal domain of the rEP3alpha-R was mutated to Ala and both isoforms and the receptor mutant (rEP3alpha-ST341-349A-R) were stably expressed in HEK293 cells. All rEP3-R receptors showed a similar ligand-binding profile. They were functionally coupled to Gi and reduced forskolin-induced cAMP-formation. Repeated exposure of cells expressing the rEP3alpha-R isoform to PGE(2) reduced the agonist induced inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP-formation by 50% and led to internalization of the receptor to intracellular endocytotic vesicles. By contrast, Gi-response as well as plasma membrane localization of the rEP3beta-R and the rEP3alpha-ST341-349A-R were not affected by prior agonist-stimulation. Agonist-stimulation of HEK293-rEP3alpha-R cells induced a time- and dose-dependent phosphorylation of the receptor most likely by G protein-coupled receptor kinases and not by protein kinase A or protein kinase C. By contrast, upon agonist-stimulation the rEP3beta-R was not phosphorylated and the rEP3alpha-ST341-349A-R was phosphorylated only weakly. These results led to the hypothesis that agonist-induced desensitization of the rEP3alpha-R isoform is mediated most likely by a GRK-dependent phosphorylation of Ser/Thr residues 341-349. Phosphorylation then initiates uncoupling of the receptor from Gi protein and receptor internalization.
Figures


References
-
- AMANO H., HAYASHI I., ENDO H., KITASATO H., YAMASHINA S., MARUYAMA T., KOBAYASHI M., SATOH K., NARITA M., SUGIMOTO Y., MURATA T., YOSHIMURA H., NARUMIYA S., MAJIMA M. Host prostaglandin E2 EP3 signaling regulates tumor-associated angiogenesis and tumor growth. J. Exp. Med. 2003;197:221–232. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BOIE Y., STOCCO R., SAWYER N., SLIPETZ D.M., UNGRIN M.D., NEUSCHÄFER-RUBE F., PÜSCHEL G.P., METTERS K.M., ABRAMOVITZ M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;340:227–241. - PubMed
-
- COLEMAN R.A., SMITH W.L., NARUMIYA S. International Union of Pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and structure of the receptors and their subtypes. Pharmacol. Rev. 1994;46:205–229. - PubMed
-
- FERGUSON S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: the role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002;53:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

