Neuroprotection by Brazilian Green Propolis against In vitro and In vivo Ischemic Neuronal Damage
- PMID: 15937561
- PMCID: PMC1142190
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/neh078
Neuroprotection by Brazilian Green Propolis against In vitro and In vivo Ischemic Neuronal Damage
Abstract
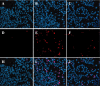
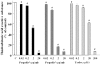
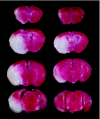
We examined whether Brazilian green propolis, a widely used folk medicine, has a neuroprotective function in vitro and/or in vivo. In vitro, propolis significantly inhibited neurotoxicity induced in neuronally differentiated PC12 cell cultures by either 24 h hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) exposure or 48 h serum deprivation. Regarding the possible underlying mechanism, propolis protected against oxidative stress (lipid peroxidation) in mouse forebrain homogenates and scavenged free radicals [induced by diphenyl-p-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH). In mice in vivo, propolis [30 or 100 mg/kg; intraperitoneally administered four times (at 2 days, 1 day and 60 min before, and at 4 h after induction of focal cerebral ischemia by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion)] reduced brain infarction at 24 h after the occlusion. Thus, a propolis-induced inhibition of oxidative stress may be partly responsible for its neuroprotective function against in vitro cell death and in vivo focal cerebral ischemia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brazilian green propolis protects against retinal damage in vitro and in vivo.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006 Mar;3(1):71-7. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nek005. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006. PMID: 16550226 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline inhibits oxidative stress and decreases in vitro and in vivo ischemic neuronal damage.Brain Res. 2005 May 17;1044(1):8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.02.062. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15862784
-
Thalidomide protects against ischemic neuronal damage induced by focal cerebral ischemia in mice.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 17;159(2):760-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.043. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19166916
-
Prevention of in vitro and in vivo acute ischemic neuronal damage by (2S)-1-(4-amino-2,3,5-trimethylphenoxy)-3-{4-[4-(4-fluorobenzyl) phenyl]-1-piperazinyl}-2-propanol dimethanesulfonate (SUN N8075), a novel neuroprotective agent with antioxidant properties.Neuroscience. 2007 Nov 23;149(4):779-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.08.029. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17945433
-
Clenbuterol protects mouse cerebral cortex and rat hippocampus from ischemic damage and attenuates glutamate neurotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons by induction of NGF.Brain Res. 1996 Apr 22;717(1-2):44-54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01567-1. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8738252
Cited by
-
Regulatory T Cells, a Potent Immunoregulatory Target for CAM Researchers: Modulating Allergic and Infectious Disease Pathology (II).Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006 Jun;3(2):209-15. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nel020. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006. PMID: 16786050 Free PMC article.
-
San-Huang-Xie-Xin-Tang Protects against Activated Microglia- and 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in Neuronal SH-SY5Y Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:429384. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep025. Epub 2011 Jan 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 19339484 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of ethanol extracts of chinese propolis (poplar type) and poplar gums based on the antioxidant activities and molecular mechanism.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:307594. doi: 10.1155/2015/307594. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25802536 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous extract of brazilian green propolis: primary components, evaluation of inflammation and wound healing by using subcutaneous implanted sponges.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:748283. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep112. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 19690045 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of microglial neurotoxicity: focus on natural products.Molecules. 2011 Jan 25;16(2):1021-43. doi: 10.3390/molecules16021021. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21350391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stapf C, Mohe JP. Ischemic stroke therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:453–75. - PubMed
-
- Sandercock P, Willems H. Medical treatment of acute ischaemic stroke. Lancet. 1992;339:537–9. - PubMed
-
- Sila CA. Prophylaxis and treatment of stroke. Drugs. 1993;45:329–37. - PubMed
-
- Flamm ES, Demopoulos HB, Seligman ML, Poser RG, Ransohoff J. Free radicals in cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1978;9:445–7. - PubMed
-
- Hara H, Sukamoto T, Kogure K. Mechanism and pathogenesis of ischemia-induced neuronal damage. Prog Neurobiol. 1993;40:645–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

