Preliminary evaluation of whole-blood gamma interferon release for clinical assessment of cellular immunity in patients with active coccidioidomycosis
- PMID: 15939743
- PMCID: PMC1151974
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.12.6.700-704.2005
Preliminary evaluation of whole-blood gamma interferon release for clinical assessment of cellular immunity in patients with active coccidioidomycosis
Abstract
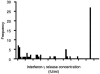
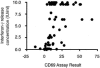
Assessment of the cellular immune response in coccidioidomycosis has epidemiologic and prognostic importance. Measurement of delayed-type hypersensitivity to skin testing has been used in the past to determine cellular immunity in coccidioidomycosis. However, no skin tests are currently available in the United States. Assay of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) release in whole blood in response to incubation with antigen has been used to assess cellular immunity in tuberculosis. We used a similar assay using the coccidioidal antigen preparation T27K to measure the in vitro cellular immune responses among a cohort of 69 subjects with active coccidioidomycosis. IFN-gamma release was bimodal, with concentrations above and below 5 IU/ml. Using multivariate logistic regression, underlying disease and disseminated or chronic pulmonary coccidioidomycosis was significantly associated with the release of IFN-gamma at a concentration of <5 IU/ml (P = 0.02 or 0.05, respectively). In addition, the release IFN-gamma concentration was <5 IU/ml in all subjects with a clinical severity score of > or =6 (P = 0.02). The release IFN-gamma concentration correlated with expression of CD69 on T lymphocytes in an in vitro assay using T27K as the antigen (Spearman's rho = 0.59; P < 0.01). These results suggest that the IFN-gamma release assay with T27K as the antigen may be a useful clinical test for assessing cellular immunity in patients with active coccidioidomycosis.
Figures
References
-
- Ampel, N. M. 2003. Measurement of cellular immunity in human coccidioidomycosis. Mycopathologia 156:247-262. - PubMed
-
- Ampel, N. M., G. C. Bejarano, S. D. Salas, and J. N. Galgiani. 1992. In vitro assessment of cellular immunity in human coccidioidomycosis: relationship between dermal hypersensitivity, lymphocyte transformation, and lymphokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 165:710-715. - PubMed
-
- Ampel, N. M., and L. A. Kramer. 2003. In vitro modulation of cytokine production by lymphocytes in human coccidioidomycosis. Cell. Immunol. 221:115-121. - PubMed
-
- Ampel, N. M., L. A. Kramer, K. M. Kerekes, S. M. Johnson, and D. Pappagianis. 2001. Assessment of the human cellular immune response to T27K, a coccidioidal antigen preparation, by flow cytometry of whole blood. Med. Mycol. 39:315-320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

