Engineered single-chain dimeric streptavidins with an unexpected strong preference for biotin-4-fluorescein
- PMID: 15939877
- PMCID: PMC1150841
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503112102
Engineered single-chain dimeric streptavidins with an unexpected strong preference for biotin-4-fluorescein
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 1;102(44):16119
Abstract
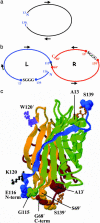
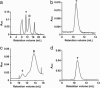
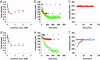
Streptavidin, a homotetrameric protein with extremely tight biotin binding (K(d) < or = 10(-14) M), has been widely used as an affinity reagent. Its utility would be increased by engineering single-chain mutants with a wide spectrum of affinities, more suitable for phage-display and chip technologies. By a circular permutation procedure, we converted streptavidin to a single-chain dimer (SCD) with two biotin-binding sites and introduced random mutations by error-prone PCR. Clones from a phagemid library, expressed as gene-3 fusion proteins on M13 bacteriophage, were panned with biotinylated beads, and SCD genes from affinity-enriched phage were subcloned to produce soluble proteins. Purification of products from the original gene and two mutants by FPLC and analysis by MALDI-TOF MS showed they exist in both dimeric (single-chain) and tetrameric (two-chain) forms, which were further characterized for their binding affinity to biotin-4-fluorescein (B4F) by fluorescence polarization and intensity measurements. K'(d) values for B4F ranged from approximately 10(-11) to 10(-10) M, although K(d) values for biotin ranged from 10(-6) to 10(-5) M. These results point to the possibility of combining an SCD streptavidin mutant with B4F derivatives to create a fluorescence-tagged affinity system with tight but still-reversible interaction that could be used sequentially with ordinary streptavidin-biotin for composite separation or analysis steps.
Figures

References
-
- Green, N. M. (1990) Methods Enzymol. 184, 51-67. - PubMed
-
- Wilchek, M. & Bayer, E. A. (1990) Methods Enyzmol. 184, 5-45. - PubMed
-
- Wilbur, D., Pathare, P., Hamlin, D., Stayton, P., To, R., Klumb, L., Buhler, K. & Vessella, R. (1999) Biomol. Eng. 16, 113-118. - PubMed
-
- Hamblett, K. J., Kegley, B. B., Hamlin, D. K., Chyan, M. K., Hyre, D. E., Press, O. W., Wilbur, D. S. & Stayton, P. S. (2002) Bioconjug. Chem. 13, 588-598. - PubMed
-
- Demidov, V. V., Bukanov, N. O. & Frank-Kamenetskii, D. (2000) Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2, 31-35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

