Two CD1 genes map to the chicken MHC, indicating that CD1 genes are ancient and likely to have been present in the primordial MHC
- PMID: 15939887
- PMCID: PMC1150808
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409213102
Two CD1 genes map to the chicken MHC, indicating that CD1 genes are ancient and likely to have been present in the primordial MHC
Abstract
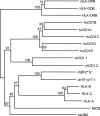
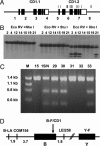
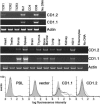
CD1 molecules play an important role in the immune system, presenting lipid-containing antigens to T and NKT cells. CD1 genes have long been thought to be as ancient as MHC class I and II genes, based on various arguments, but thus far they have been described only in mammals. Here we describe two CD1 genes in chickens, demonstrating that the CD1 system was present in the last common ancestor of mammals and birds at least 300 million years ago. In phylogenetic analysis, these sequences cluster with CD1 sequences from other species but are not obviously like any particular CD1 isotype. Sequence analysis suggests that the expressed proteins bind hydrophobic molecules and are recycled through intracellular vesicles. RNA expression is strong in lymphoid tissues but weaker to undetectable in some nonlymphoid tissues. Flow cytometry confirms expression from one gene on B cells. Based on Southern blotting and cloning, only two such CD1 genes are detected, located approximately 800 nucleotides apart and in the same transcriptional orientation. The sequence of one gene is nearly identical in six chicken lines. By mapping with a backcross family, this gene could not be separated from the chicken MHC on chromosome 16. Mining the draft chicken genome sequence shows that chicken has only these two CD1 genes located approximately 50 kb from the classical class I genes. The unexpected location of these genes in the chicken MHC suggests the CD1 system was present in the primordial MHC and is thus approximately 600 million years old.
Figures

Comment in
-
Bird genes give new insights into the origins of lipid antigen presentation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8399-400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503313102. Epub 2005 Jun 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15939875 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Flajnik, M. & Kasahara, M. (2001) Immunity 15, 351-362. - PubMed
-
- Kasahara, M., Suzuki, T. & Du Pasquier, L. (2004) Trends Immunol. 25, 105-111. - PubMed
-
- Eason, D., Cannon, J., Haire, R., Rast, J., Ostrov, D. & Litman, G. (2004) Semin. Immunol. 16, 215-226. - PubMed
-
- Porcelli, S. & Modlin, R. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 297-329. - PubMed
-
- Jayawardena-Wolf, J. & Bendelac, A. (2001) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 109-113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

