Surface CD88 functionally distinguishes the MCTC from the MCT type of human lung mast cell
- PMID: 15940129
- PMCID: PMC1460014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.02.022
Surface CD88 functionally distinguishes the MCTC from the MCT type of human lung mast cell
Abstract
Background: MC(T) and MC(TC) types of human mast cells (MCs) are distinguished from one another on the basis of the protease compositions of their secretory granules, but their functional and developmental relationships have been uncertain.
Objective: These studies better define the functional properties and developmental relationship of MC(T) and MC(TC) cells.
Methods: Mast cells were dispersed from human skin and lung, purified with anti-Kit antibody, and separated into CD88+ and CD88- populations by cell sorting. These cells were evaluated by immunocytochemistry with antitryptase and antichymase mAbs; for chymase and tryptase mRNA by real-time RT-PCR; for conversion of MC(T) to MC(TC) cells during cell culture with recombinant human stem cell factor and recombinant human IL-6; and for degranulation and leukotriene C 4 (LTC 4 ) secretion when stimulated with anti-FcepsilonRI, substance P, C5a, and compound 48/80.
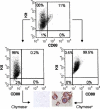
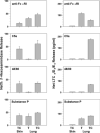
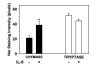
Results: Mature MC(T) and MC(TC) cells were separated from one another on the basis of selective expression of CD88, the C5aR, on MC(TC) cells. Lung MC(T) cells had negligible levels of chymase mRNA and retained their MC(T) phenotype in culture. Mature MC(TC) cells from skin and lung degranulated in response to FcepsilonRI cross-linking, C5a, compound 48/80, and substance P. Lung MC(TC) cells released LTC 4 on activation, but no LTC 4 was detected when skin-derived MC(TC) cells were activated. MC(T) cells from lung degranulated and released LTC 4 in response to anti-FcepsilonRI and substance P, but not to C5a and compound 48/80.
Conclusion: These observations functionally distinguish MC(T) from MC(TC) types of human mast cells and suggest important differences that may affect their participation in diseases such as asthma and urticaria.
Figures
References
-
- Irani A-MA, Goldstein SM, Wintroub BU, Bradford T, Schwartz LB. Human mast cell carboxypeptidase: selective localization to MCTC cells. J Immunol. 1991;147:247–53. - PubMed
-
- Schechter NM, Irani A-MA, Sprows JL, Abernethy J, Wintroub B, Schwartz LB. Identification of a cathepsin G-like proteinase in the MCTC type of human mast cell. J Immunol. 1990;145:2652–61. - PubMed
-
- Brightling CE, Bradding P, Symon FA, Holgate ST, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Mast-cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1699–705. - PubMed
-
- Gibson PG, Allen CJ, Yang JP, Wong BJO, Dolovich J, Denburg J, et al. Intraepithelial mast cells in allergic and nonallergic asthma: assessment using bronchial brushings. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;148:80–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

